Fig. 5.
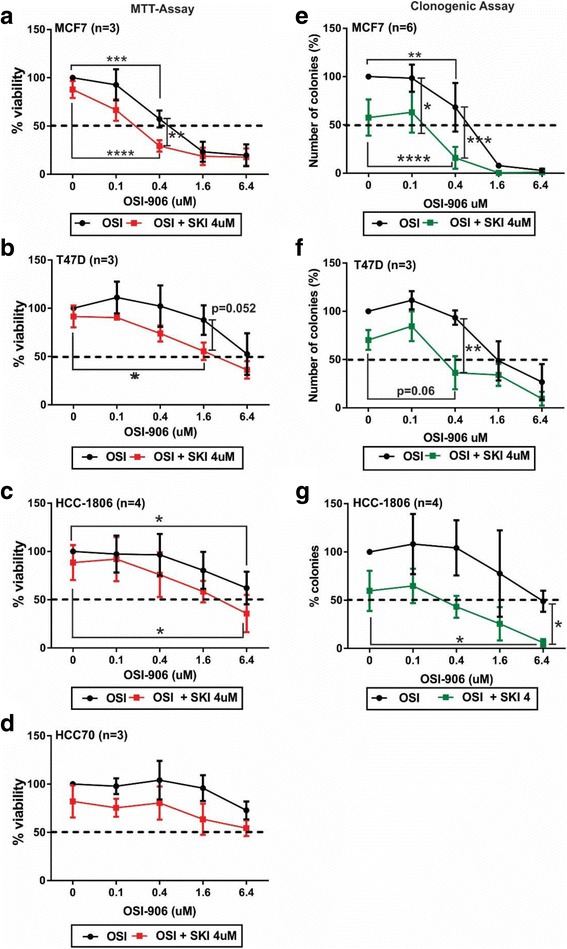
Co-targeting IGF1R and SphK1 effects on cell viability and colony formation in breast cancer cells. a-d. MTT-assay and (e-g). colony formation experiments were performed using the ER-positive; MCF7 and T47D and ER-negative; HCC1806 and HCC70 breast cancer cell-lines. 2 × 103 cells were plated in either 96-well or 6-well plates, cultured for 24 h and subsequently treated with the dual IGF1R/InsR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (OSI-906; 0.1-6.4 μM) and/or SphK1inhibitor (SKI-II; 4 μM) for 96 h (MTT-assay) and 10-14 d (clonogenic assay). Repeated measures ANOVA was performed to determine the effect of SKI-II addition to OSI-906 does-response curves. Graphs depict experimental data normalized to zero treatment vehicle control and 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test was performed to determine significance between treatment groups and significance accepted p-values *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. All experiments were performed in triplicate for MTT-assay and duplicate for clonogenic assay. Note: The SKI 4 μM plus OSI 6.4 μM treatment was only performed in duplicate for the HCC1806 clonogenic assay experiments
