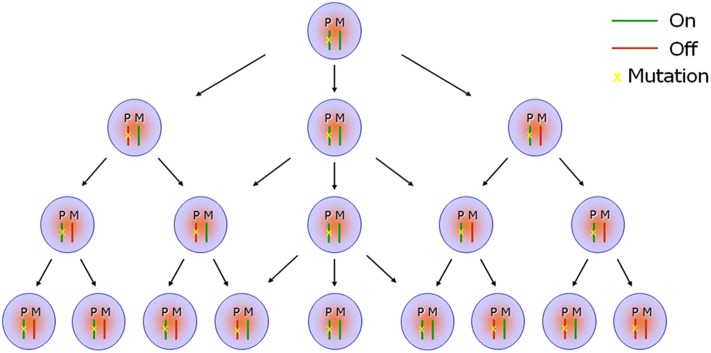
FIGURE 2.
Scheme of monoallelic expression in developing organs. Random monoallelic expression (RME) occurs in maternal or paternal alleles (i.e., turned “On” or turned “Off”) stochastically in the developing embryos, which results in a mosaic expression signature (monoallelic, biallelic, or null) in a specific tissue or across different tissues. When one of the parental alleles is mutant—for example, the paternal allele as indicated in the scheme (P: paternal; M: maternal)—the mosaic expression profile further generates co-existence of discrepant protein composition or function in a proportion of cells, attributable to random inactivation of the wild-type maternal allele. For instance, cells showing haploinsufficiency for a particular gene will co-exist alongside cells completely lacking functional protein when the gene mutation is loss-of-function.