Figure 3. αSyn-dependent microglia activation by the microbiota.
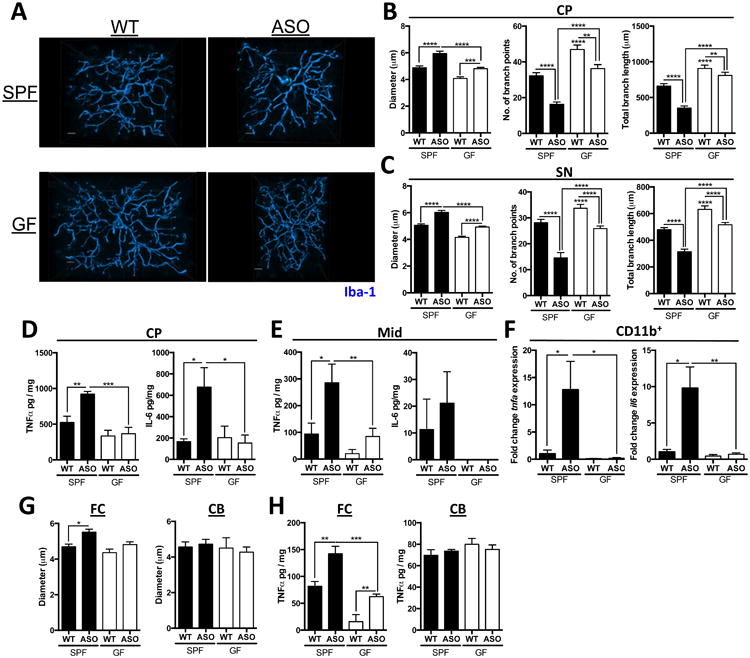
(A) Representative 3D reconstructions of Iba1-stained microglia residing in the caudoputamen (CP) of SPF-WT, SPF-ASO, GF-WT, and GF-ASO animals
(B) CP-resident microglia parameters diameter, number of branch points, and total branch length
(C) Substantia nigra (SN)-resident microglia parameters diameter, number of branch points, and total branch length
(D) ELISA analysis for TNF-α and IL-6 present in homogenates from the CP
(E) ELISA analysis for TNF-α and IL-6 present in homogenates from the inferior midbrain (Mid)
(F) qPCR analysis of CD11b+ cells derived from brain homogenate for tnfa and il6
(G) Diameter of microglia residing in the frontal cortex (FC) or cerebellum (CB)
(H) ELISA analysis for TNF-α present in homogenates from the FC or CB
Tissues collected from mice at 12-13 weeks of age. N=3-4, (with 20-60 cells per region per animal analyzed) error bars represent the mean and standard error. *p ≤ 0.05; **p≤ 0.01; ***p≤ 0.001; ****p≤ 0.0001. SPF=specific pathogen free, GF=germ-free, WT=wild-type, ASO=Thy1-α-synuclein genotype. See also Figure S2.
