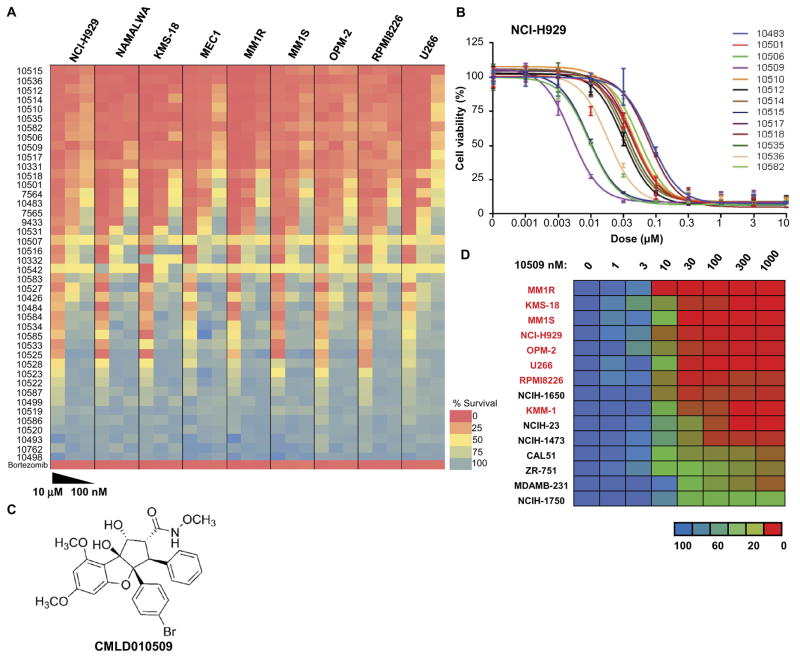
Fig. 3. High potency of rocaglate inhibitors in MM.
(A) Heat map of the effects of 40 rocaglate derivatives on relative survival of MM cells (NCI-H929, KMS-18, MM1R, MM1S, OPM-2, RPMI8226, and U266) along with lymphoma cell lines (NAMALWA and MEC1) shows strong activity with low doses of the rocaglate compounds in these cell lines. (B) IC50 of these 40 compounds in NCI-H929 showing that CMLD010509 was the most potent compound, with an IC50 below 10 nM. (C) CMLD010509 is a synthetic rocaglate derivative containing the cyclopenta[b]tetrahydrobenzofuran core structure. (D) IC50 of CMLD010509 showing an IC50 below 10 nM for most MM cell lines tested (indicated in red), whereas it was relatively resistant in lung and breast cancer cell lines (in black) with an IC50 of ~30 nM.