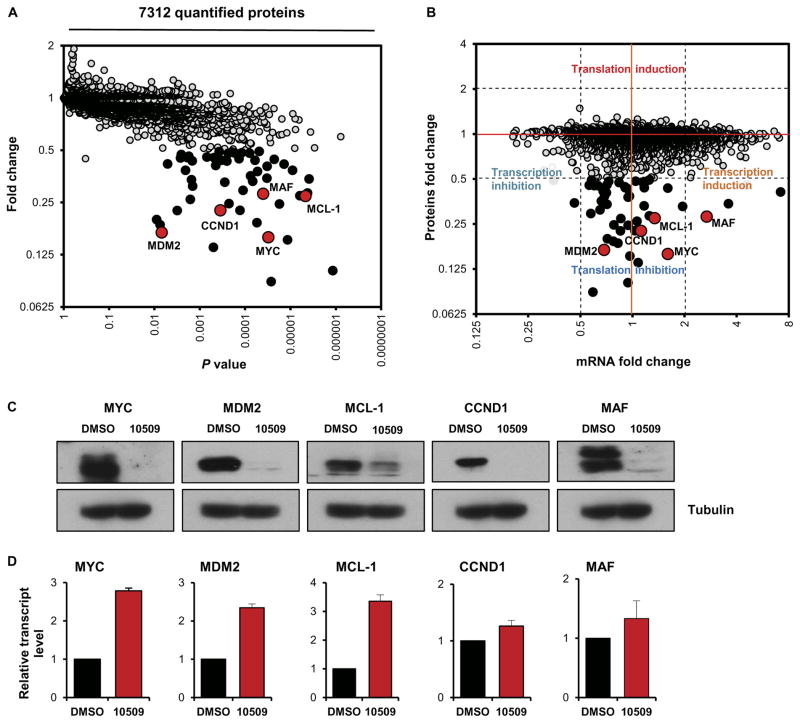
Fig. 5. Regulation of the oncogenic translation program of MM by CMLD010509.
(A) Expression proteomics showing the impact of CMLD010509 treatment (100 nM) relative to vehicle control in NCI-H929 cells after a 2-hour incubation (three biological replicates were used and individually tagged using isobaric tagging). We identified 7312 proteins, of which 54 were significantly depleted by more than twofold through CMLD010509 exposure (P < 0.05; fold change, >2). The most depleted proteins included MYC, MDM2, CCND1, MCL-1, and MAF (red dots). (B) Comparison of the protein fold changes to the transcript fold changes in CMLD010509- versus vehicle-treated cells. A large majority of depleted proteins had a transcript fold change lower than twofold, suggesting a specific translational mechanism of action for CMLD010509. (C) Immunoblots and (D) qRT-PCR analysis of MYC, MDM2, CCND1, MCL-1, and MAF in compound-treated (100 nM, 3 hours) or vehicle-treated NCI-H929. All five genes were depleted at the protein level, whereas their transcripts were unchanged or slightly overexpressed.