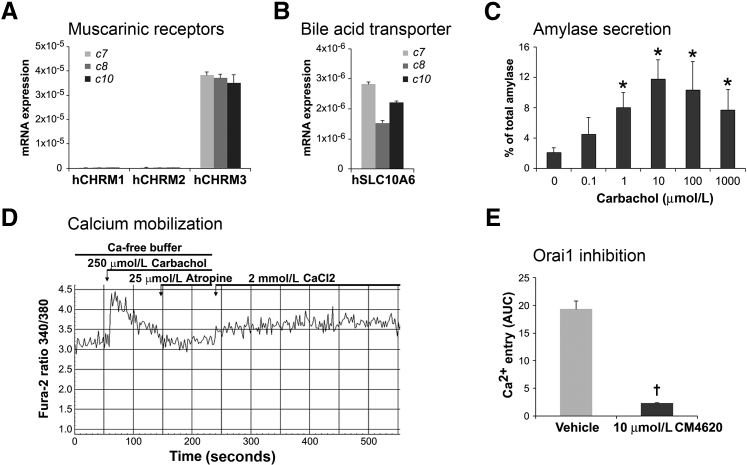
Figure 6.
Human acini express the human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 (hCHRM3) and exhibit a biphasic secretory response to cholinergic stimulation. A and B: mRNA extracts from human acini isolated from three organ donor pancreata (c7, c8, and c10 [c indicates organ donor case (patient coding) used as a source of human acinar preparation]) were analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR to determine the expression of the indicated muscarinic receptors (A) and the bile acid transporter solute carrier family 10 member 6 (SLC10A6; B). All three human acinar preparations analyzed preferentially express the muscarinic receptor CHRM3 and the SLC10A6 transporter. C: Human acini were stimulated for 30 minutes with the cholinergic agonist carbachol at the indicated concentrations, and amylase release was measured using the Phadebas test. As shown, human acinar cells respond to carbachol stimulation by releasing amylase in a typical biphasic pattern also reported for rodent acini. D and E: Characterization of carbachol-induced calcium response in human acini. Acini were loaded with Fura-2 AM and then stimulated with 250 μmol/L carbachol in the absence of free Ca2+ in the extracellular buffer. As shown, carbachol causes a rapid, transit elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ in Fura-loaded cells. Atropine was then added to terminate the Ca2+-releasing signal. Adding Ca2+ to the extracellular media (2 mmol/L CaCl2) leads to Ca2+ entry, and this effect is blocked by preincubation with CM4620, a specific inhibitor of the store-operated Ca2+ channel, Orai (E). Data are expressed as means ± SD (C and E). n = 3 independent experiments (C and E). ∗P < 0.05 versus basal (no carbachol); †P < 0.05 versus vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide). AUC, area under the curve.