Figure 1.
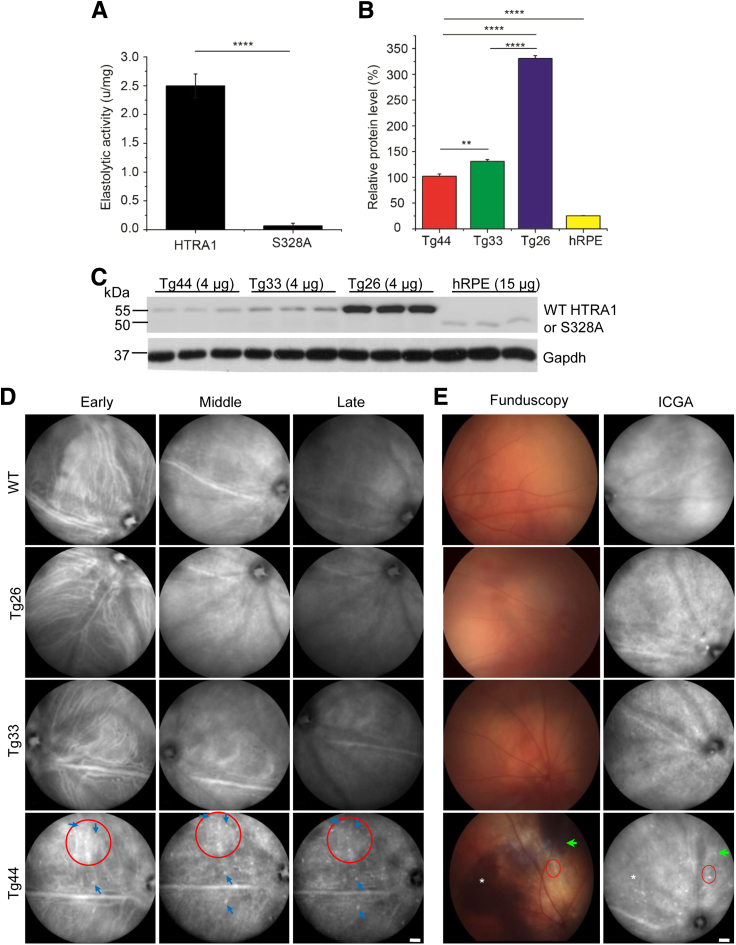
Transgenic mice Tg33 and Tg26 expressing HTRA1S328A did not develop polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV). A: Elastase assay of recombinant wild-type (WT) human HTRA1 and mutant human HTRA1S328A. Statistical significance was assessed using t-test. B and C: Western blot and quantification of human HTRA1 expression in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and choroid of Tg44 and Tg33 mice. Data showed the relative protein levels of human HTRA1 (or HTRA1S328A) signal from 4 μg of RPE/choroid lysates of Tg44 and Tg33, and 15 μg lysate of human RPE/choroid. C: The myc-His6 tagged transgenic HTRA1 and HTRA1S328A ran at 55 kDa, whereas the native HTRA1 [from human RPE (hRPE)] ran at 50 kDa. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) was included as the loading control. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way analysis of variance with post-hoc Tukey test. HTRA1 in hRPE is significantly different from all three transgenic lines (Tg44, Tg33, and Tg26; P < 0.0001). D: Early-, middle-, and late-phase indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) showed that Tg33 and Tg26 mice had normal choroidal vasculature, which was similar to WT. However, Tg44 mice developed two cardinal features of PCV, polyp dilations (blue arrows) and branching vascular network (red circles). E: Funduscopy (left column) and paired ICGA (right column). Tg44 mice exhibited reddish orange nodules corresponding to PCV lesion structures (red circles), hemorrhage (asterisks), and RPE degeneration (green arrows). Tg33 and WT controls were normal. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (A and B). n = 4 (A); n = 3 (B). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. Scale bar = 1000 μm (D and E). u, units.