Fig. 6.
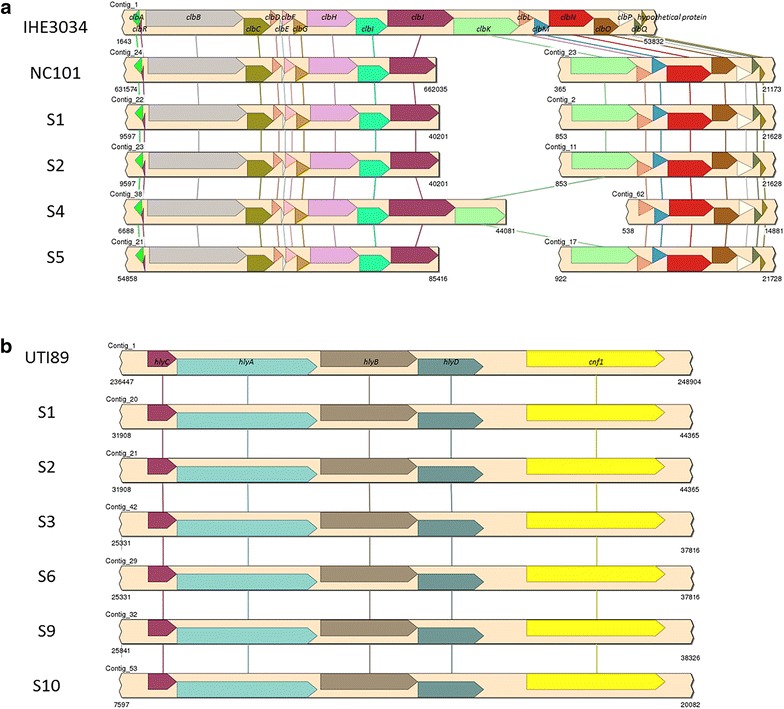
a In the draft genomes of four representative novel rhesus macaque isolates PCR-positive for the clbA and clbQ genes, complete pks pathogenicity islands were identified and had ≥ 98% sequence homology and identical syntenic relationships compared to prototype pks+ strains IHE3034 and NC101. Due to being draft genomes, the genes in pks pathogenicity islands were separated onto two different contigs for NC101 and the four novel isolates. No pks pathogenicity island genes were identified in the draft genomes of any of the pks− isolates. b In the draft genomes of six representative novel rhesus macaque isolates PCR-positive for cnf1, the hemolysin-cnf1 operon was identified and had ≥ 99% sequence homology and identical syntenic relationships compared to the prototype hemolysin-cnf1 operon of the human uropathogenic E. coli strain UTI89. Neither cnf1 nor any hemolysin genes belonging to this operon were detected in any of the draft genomes of the other representative novel isolates
