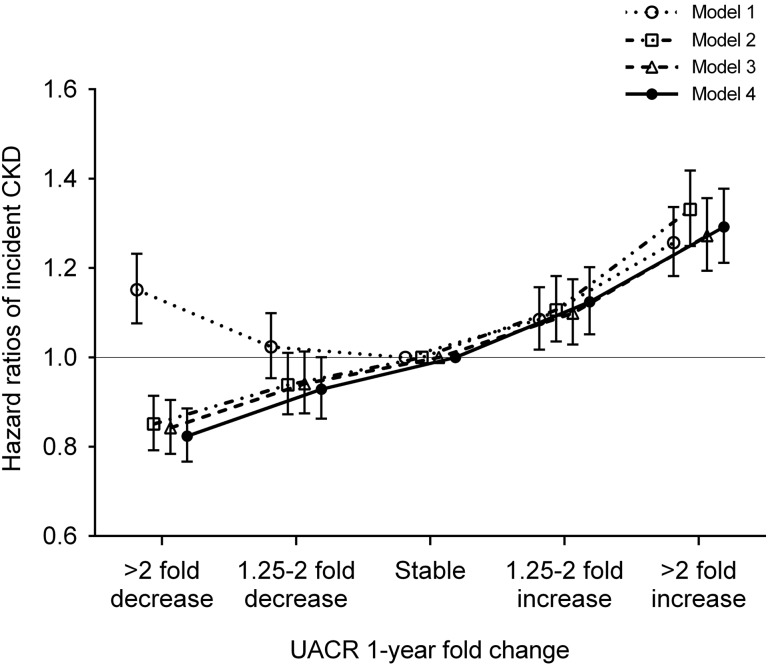
Figure 1.
The adjusted association between 1-year fold UACR changes and incident CKD showed a nearly linear relationship. Models represent unadjusted association (model 1); associations after adjustment for age, sex, race, baseline eGFR, and log-transformed UACR (model 2); model 2 variables plus comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, chronic lung disease, liver disease, dementia, rheumatic disease, malignancy, depression, and HIV/AIDS; model 3); and model 3 plus baseline body mass index, systolic BP, diastolic BP, slopes of systolic BP and eGFR, use of statins and nonopioid analgesics at baseline, renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) treatment status (four categories on the basis of RASi use at the dates of the first and last UACR measurements during the baseline period [i.e., use at both, either, or neither dates]), and RASi adherence (model 4).