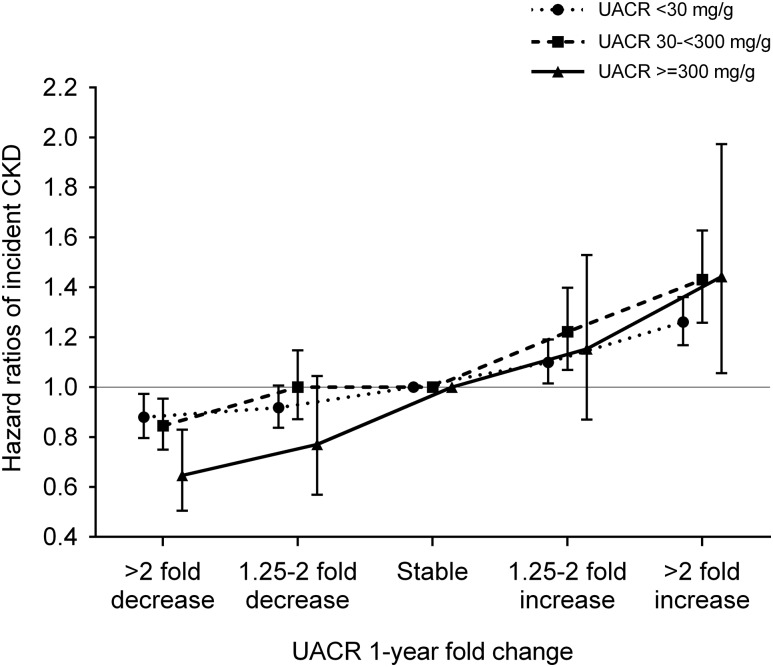
Figure 2.
A similar trend of association was observed in patients with different baseline UACR levels. Data are adjusted for age, sex, race, baseline eGFR, log-transformed UACR, comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, chronic lung disease, liver disease, dementia, rheumatic disease, malignancy, depression, and HIV/AIDS), baseline body mass index, systolic BP, diastolic BP, slopes of systolic BP and eGFR, use of statins and nonopioid analgesics at baseline, renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) treatment status (four categories on the basis of RASi use at the dates of the first and last UACR measurements during the baseline period [i.e., use at both, either, or neither dates]), and RASi adherence. P for interaction =0.05.