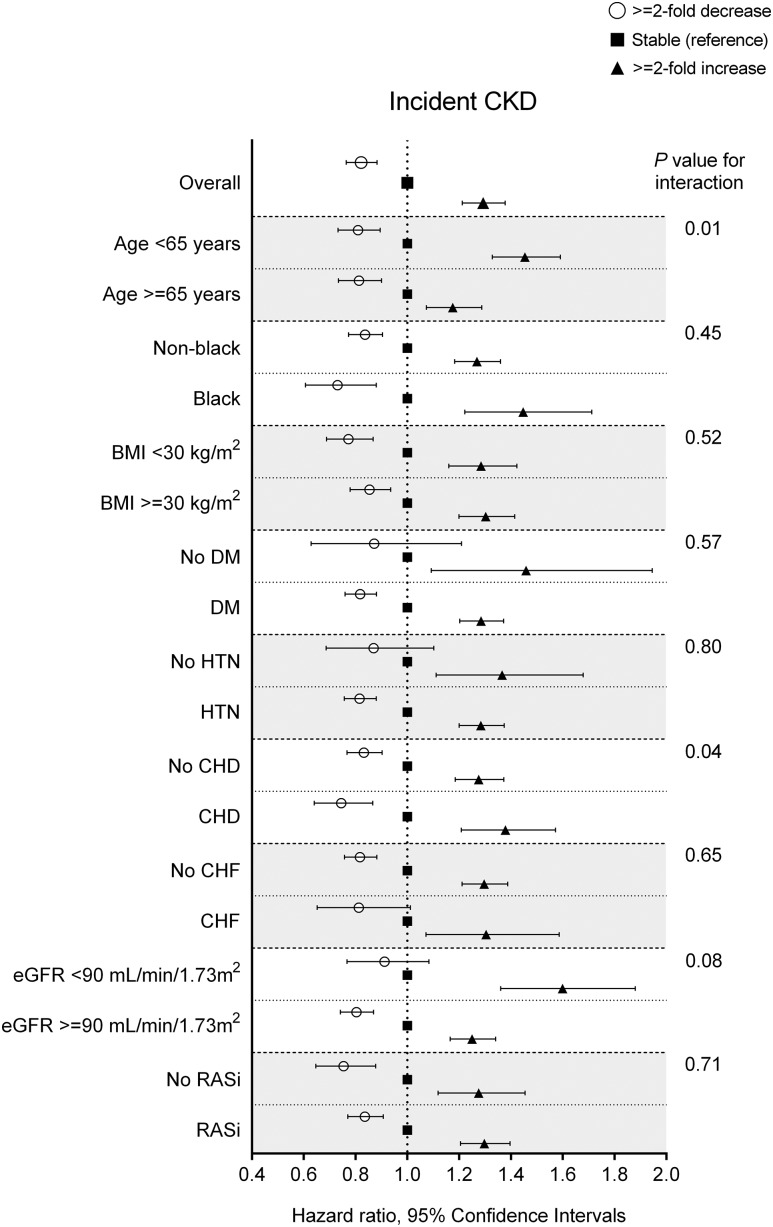
Figure 3.
The associations of 1-year fold UACR changes with incident CKD were generally consistent across subgroups. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) indicates patients with any exposure to RASi between the first and last UACR measurement during the 2-year baseline period. Data are adjusted for age, sex, race, baseline eGFR, log-transformed UACR, comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, chronic lung disease, liver disease, dementia, rheumatic disease, malignancy, depression, and HIV/AIDS), baseline body mass index, systolic BP, diastolic BP, slopes of systolic BP and eGFR, use of statins and nonopioid analgesics at baseline, RASi treatment status (four categories on the basis of RASi use at the dates of the first and last UACR measurements during the baseline period [i.e., use at both, either, or neither dates]), and RASi adherence. CHD, coronary heart disease; CHF, congestive heart failure; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension.