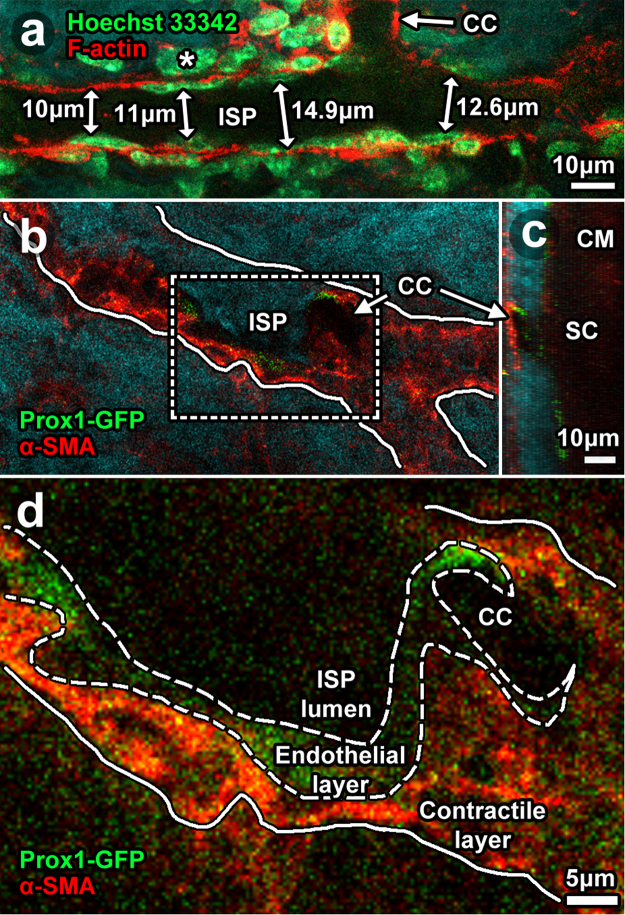
Figure 10.
Cellular arrangement in distal aqueous drainage tract walls. 2-photon imaging ex vivo after labeling with: Hoechst 33342 for nuclei (a; C57BL/6 mouse eyes); phalloidin-Alexa-568 for F-actin (a); and anti-alpha-smooth muscle actin antibodies (ASMA in Prox1-GFP mouse eyes; (b–d). (a) A thin cellular layer with flat nuclei lay next to the lumen (dark signal void) of an intrascleral plexus (ISP) connecting with a collector channel. This Prox1-GFP-positive layer (b, low magnification; (c), orthogonal reconstruction; (d), high magnification) was consistent with distal tract endothelium. A multilayered cellular layer external and adjacent to the endothelium had plump nuclei and expressed ASMA but not Prox1-GFP. This ASMA-positive layer was consistent with a contractile smooth muscle layer. It correlated with the ASMA-, calponin- and caldesmon-positive regions that prominently co-localized with F-actin labeling shown in Fig. 9. Double-sided arrows represent ISP lumen diameter measurements nearest the collector channel ostium (CCO).