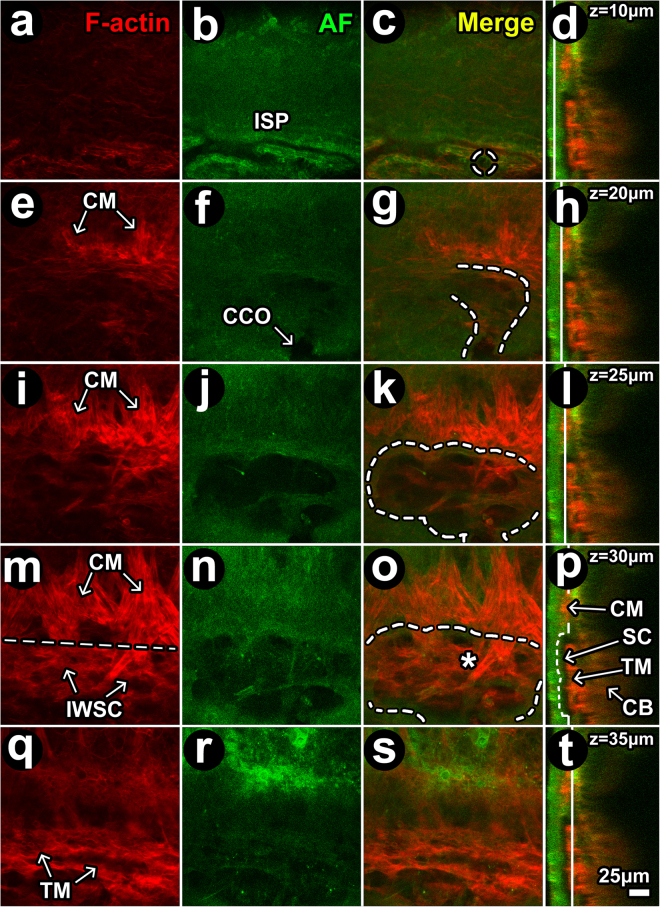
Figure 11.
Filamentous actin in proximal and distal aqueous drainage tract. (a–d) at z = 10 μm (from the external scleral surface), autofluorescence (AF; green) signal voids (dark) revealed intrascleral plexuses (ISP) lined by filamentous actin (F-actin; red). Dashed circle: location of ostium more proximally in Schlemm’s canal (SC). (e–h) At z = 20 μm, F-actin-positive ciliary muscle (CM) fibers oriented perpendicular to ISP attach at a border region posterior to SC analogous to scleral spur. Curved dashed line: outlines SC lumen within a scleral depression (AF signal void). (i–l) At z = 25 μm, more proximal in SC lumen (j; dashed outline in k), F-actin-positive CM fibers were more prominent and crossed into the region of SC (within dashed outline) within the trabecular meshwork (TM)/inner wall of SC (SCIW) interface. (m–p) At z = 30 μm, vertically-oriented F-actin-positive CM fibers intermingle with cellular F-actin in the TM/IWSC interface region. Horizontal line places an imaginary border between CM and TM/IWSC regions (asterisk). The AF signal (j,n) revealed septae and loculation in SC. (q–t) At z = 35 μm, an F-actin-positive mesh-like labeling pattern was seen in the TM. Red: F-actin (a,e,i,m,q). Green: AF from structural extracellular matrix (b,f,j,n,r). Merged optical sections: (c,g,k,o,s) (red-green). Merged orthogonal reconstructions: (d,h,l,p,t) (red-green). Vertical white line in orthogonal image: z-location of optical section. Curved dashed lines: outline a lumen that continued from ISP to collector channel (CC; dashed circle) to CC opening (CCO) to SC.