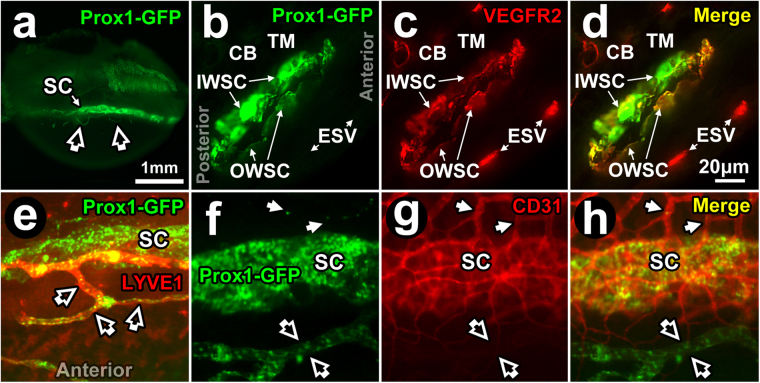
Figure 4.
Prox1-GFP expression in Schlemm’s canal. (a) Prox1-GFP expression (bright green band) in Prox1-GFP mouse Schlemm’s canal (SC) seen by imaging the external limbus ex vivo (external eye surface faces reader). The cornea lies inferiorly. Open arrows: anterior Prox1-GFP-positive anterior projections from limbal lymphatics (see later Fig. 5). (b–d) Fluorescence microscopy of a frozen section (10 μm thickness) of Prox1-GFP mouse angle tissue after labeling with anti-VEGFR2 antibodies. (b) At higher magnification, Prox1-GFP expression was more intense in the inner wall (IWSC) than outer wall of SC (OWSC). Prox1-GFP expression was not seen in the trabecular meshwork (TM), ciliary body (CB), and episcleral vessels (ESV). (c) VEGFR2 staining intensity was similar in IWSC, OWSC, CB blood vessels and episcleral veins (ESV). (d) A merged image shows Prox1-GFP co-localization with VEGFR2 in IWSC and OWSC but not ESV. (e) Merged image showing Prox1-GFP and LYVE-1 expression. Prox1-GFP is expressed in both SC (green) and lymphatic vessels (open arrows) but only lymphatic vessels express LYVE-1 that co-localizes with Prox1 (orange). (f–h) SC, lymphatic vessels (open arrows) and blood vessels (closed arrows) at the limbus. (f) Prox1 (green) is expressed in SC and lymphatic vessels but not blood vessels. (g) CD31 (red) is expressed in SC and blood vessels but is low in lymphatic vessels. (h) Merged image shows Prox1 and CD31 co-localization in SC (orange) but not in blood vessels (red) or lymphatic vessels (green).