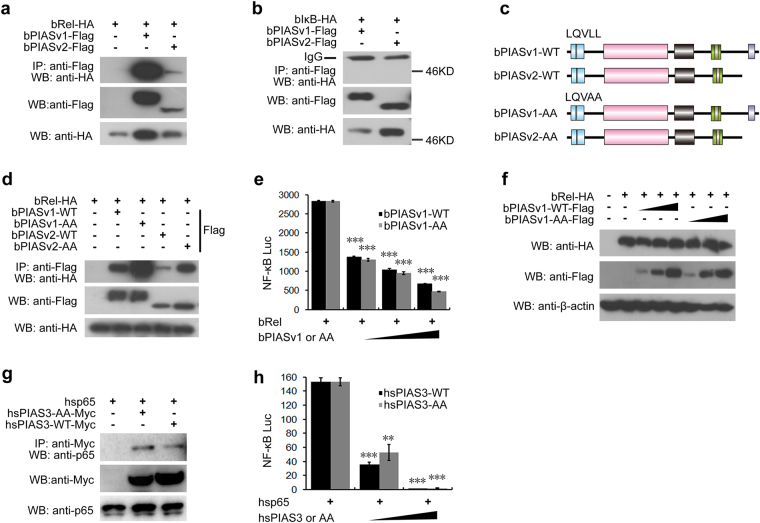
Figure 3.
Amphioxus PIAS interacts with NF-κB Rel, and the LXXLL motif in bPIAS is not required for binding and inhibiting bRel. (a,b) Co-IP analyses of the interactions between bPIAS and bRel (a) or bIκB (b). (c) The bPIAS-(LL-AA) point mutants used in this study. (d) Co-IP assays indicate that the bPIAS-AA point mutant is also capable of binding to bRel, similar to its wild-type counterpart. (e) Luciferase reporter assays show that bPIAS-AA can inhibit bRel-dependent transcription activation to the same extent as the wild-type bPIAS. (f) Western blot was performed to show the expression of relevant proteins, including bPIAS-WT, bPIAS-AA and bRel, β-actin was used as the internal reference. (g) Co-IP assays indicate that the hsPIAS3-AA point mutant is also capable of binding to hsp65, similar to its wild-type counterpart. (h) Luciferase reporter assays show that hsPIAS3-AA can inhibit hsp65-dependent transcription activation to the same extent as the wild-type hsPIAS3. Data show a representative result from at least three separate experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.