Figure 1.
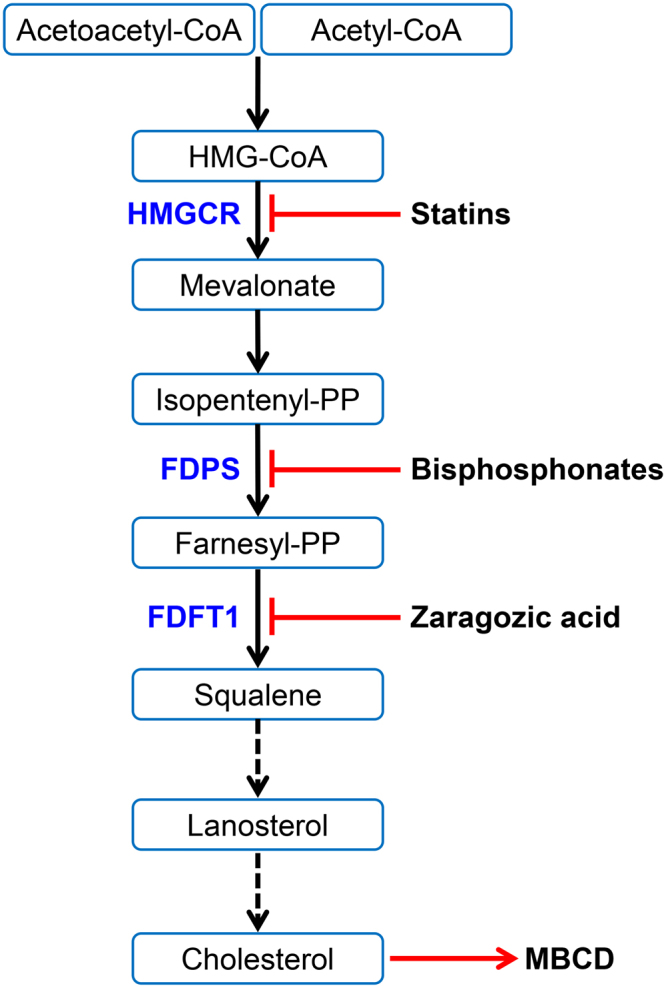
The mevalonate pathway leads to cholesterol synthesis. Acetoacetyl CoA and acetyl CoA are converted to squalene, which is subsequently converted to cholesterol. Important enzymes in the pathway include 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FDPS), and farnesyl diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1 (FDFT1, also commonly called squalene synthase). Each of these enzymes can be inhibited by statins, bisphosphonates, and zaragozic acid, respectively; cholesterol can be depleted using methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MBCD).
