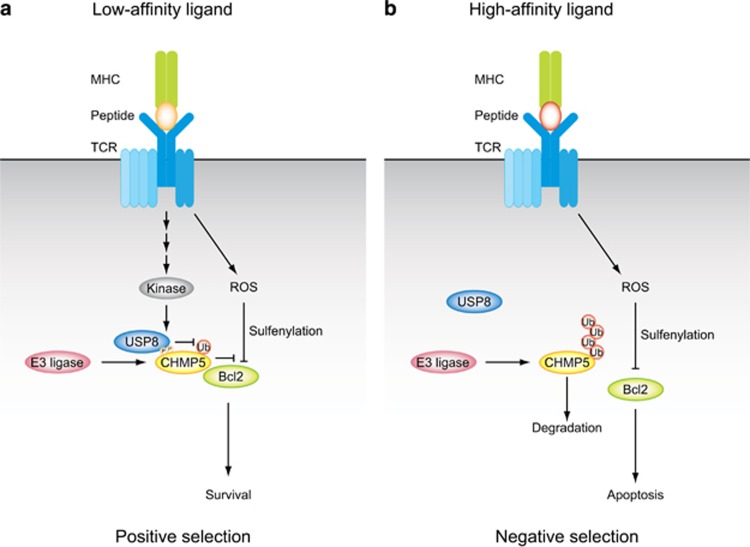
Figure 1.
Models for post-translational control of CHMP5 during T-cell development. (a) When TCR is stimulated by low-affinity ligands, an unknown kinase activated by TCR signaling phosphorylates CHMP5 at Ser26 and Ser30, leading to recruitment of a deubiquitinating enzyme, USP8. USP8 stabilizes CHMP5 via its deubiquitination. Increased CHMP5 proteins directly bind to Bcl-2 and prevent reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated sulfenylation of Bcl-2 and subsequent degradation. These processes result in survival of thymocytes. (b) When TCR is stimulated by high-affinity ligands, CHMP5 is ubiquitinated and degraded via the proteasome pathway. CHMP5 proteins fail to prevent ROS-mediated sulfenylation and degradation of Bcl-2. These processes result in apoptosis of thymocytes. CHMP, charged MVB protein; TCR, T-cell receptor.