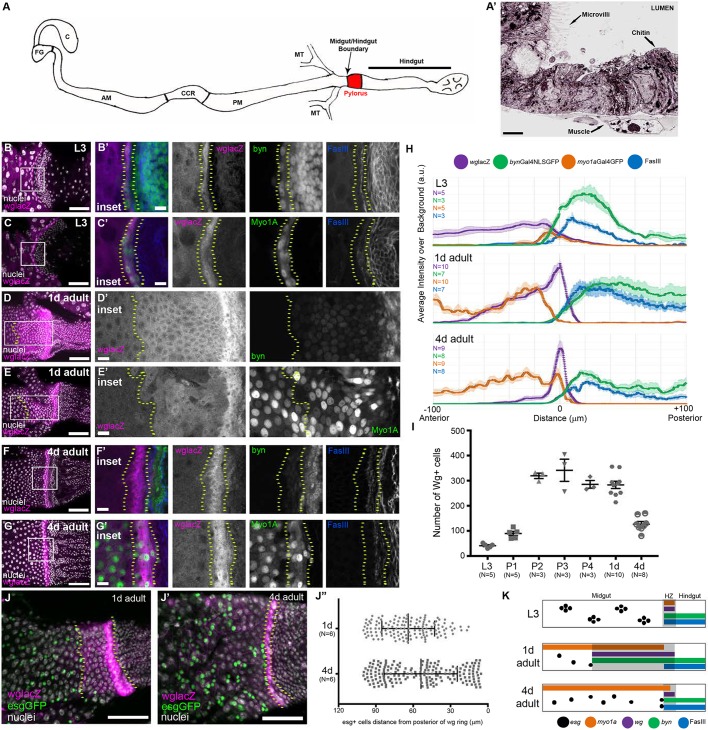
Fig. 1.
The Wg ring is a dynamic HZ adjacent to midgut ISCs/EBs. (A) Schematic of the Drosophila intestine. AM, anterior midgut; C, crop; CCR, copper cell region; FG, foregut; MT, malpighian tubules; PM, posterior midgut. (A′) Electron micrograph illustrating the phenotypic differences at the midgut/hindgut boundary. There is a clear transition from cells with microvilli to cells that lack microvilli, but are chitin rich. (B-I) The HZ is present throughout development: L3 (B-C′), 1 day adult (D-E′), 4 days adult (F-G′). (H) Line profiles of midgut, HZ and hindgut markers. Data represent mean±s.e.m. (I) The number of wg+ cells over time, L3 to adulthood. Data represent mean±s.e.m. (J-J″) esg+ cells stay at the anterior edge of the wg expression domain. Data represent mean±s.e.m. of all esg+ cells from six animals. Unpaired, two-tailed t-test, P=0.0006. (K) Model of the HZ during development. Genotypes and markers are indicated within panels; yellow dotted lines indicate the HZ. Scale bars: 2 µm in A′; 10 µm in B′,C′,D′,E′,F′ and G′; 50 µm in B,C,D,E,F,G,J and J′.