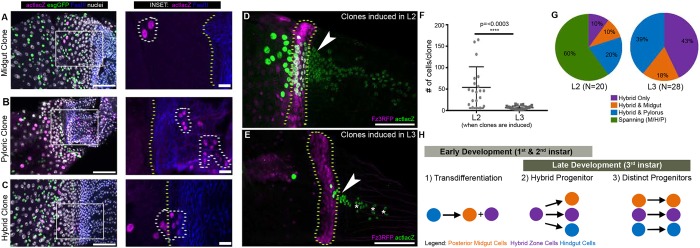
Fig. 2.
The larval HZ significantly contributes to the adult posterior midgut and anterior hindgut. (A-C) Examples of clone types observed: midgut (A), pyloric (B), hybrid (C); esgGFP marks midgut ISCs/EBs. Scale bars: 50 µm (10 µm in insets). (D) Example of a clone induced in L2 (second instar); esg was not labeled in this experiment. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) Example of a clone induced in L3 (third instar); esg was not labeled in this experiment. Scale bar: 50 µm. (F) Clones induced earlier in development that overlap the HZ are larger. Data represent mean±s.e.m. Unpaired, two-tailed t-test, unequal variance. (G) Clones that span the posterior midgut, HZ and pylorus are only observed when clones are induced early in development. Chi-Square Fisher's Exact test, P≤0.0001. (H) Models illustrating potential origins of the HZ. Genotypes and markers are indicated within panels; yellow dotted lines indicate the HZ, white dotted lines indicate clones, arrowheads indicate hybrid clones, asterisks indicate pyloric clones.