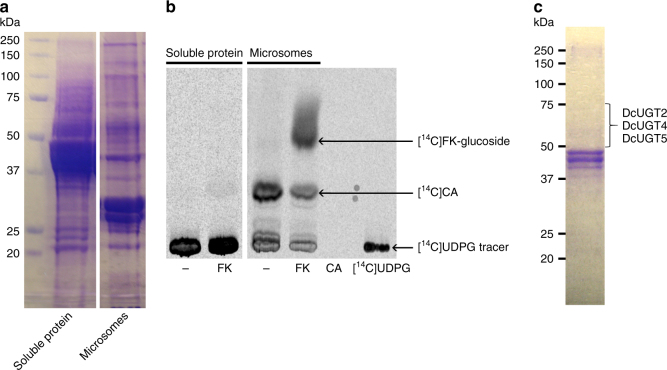
Fig. 2.
Identification of a Dactylopius coccus FK/KA-specific UGT activity. An isolated microsomal protein fraction and a soluble protein fraction from D. coccus were tested for glucosylation activity in vitro using the flavokermesic acid aglucone and the [14C]UDP-glucose donor. a Coomassie-stained SDS gel of separated microsomal/soluble protein from D. coccus. b TLC-separated [14C]-labeled products, formed in vitro and monitored by phosphorimaging. [14C]UDPG [14C]UDP-glucose, FK flavokermesic acid, CA carminic acid; − incubation without aglucone substrate. The in vitro formation of [14C]CA was ascribed to the conversion of kermesic acid that still was bound to the D. coccus microsomes despite numerous wash steps during preparation. c A membrane-bound enzyme activity catalyzing the glucosylation of flavokermesic acid and kermesic acid was partially purified by anion-exchange chromatography after solubilization with reduced Triton X-100 (Supplementary Fig. 1). A fraction eluted with 100 mM NaCl and enriched with flavokermesic acid/kermesic acid-specific glucosylation activity was separated on an SDS gel followed by Coomassie staining. Proteins within the apparent mass region of 50–75 kDa were in-gel digested with trypsin and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Tryptic peptides of DcUGT2, DcUGT4 and DcUGT5 were identified