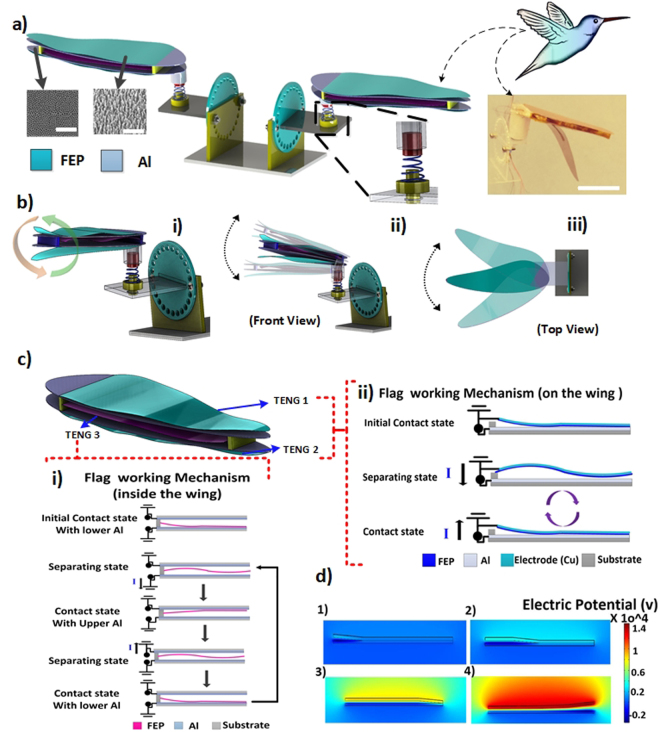
Figure 1.
Schematic and experimental structure of a hummingbird wind TENG. (a) 3D modeling of the proposed H-TENG wind harvester (with SEM photo at 1 μm scale bar for the Al surface on the left, and SEM image of the FEP polymer nanowires at sale bar is 500 nm on the right), Inset photos represent the real hummingbird bird and the real hummingbird TENG. (b) H-TENG kinematics analysis in front and top views (c) 3D model of the hummingbird wing with description of the three TENGs configurations; at the top (TENG 1), at the bottom (TENG 2) and inside the wing (TENG 3) (i) Working mechanism of the flag TENG which is placed on the top and bottom of the H-TENG harvester wing. (ii) Working mechanism of the flag inside the wing as a second mode to harvest the mechanical motion resulting from the wind and mimicking the hummingbird flapping motion, (d) Potential distribution of the device for different flags using COMSOL.