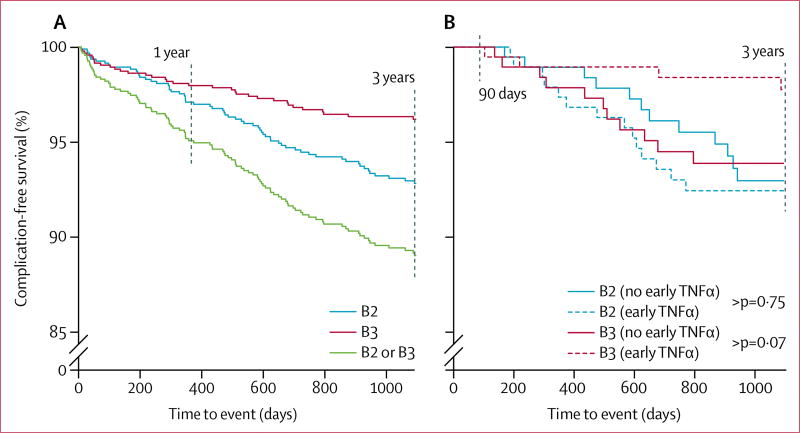
Figure 1. Development of stricturing or penetrating complications during follow-up in the competing-risk analysis in the whole cohort (A) and in the propensity-matched cohort (B).
B2 refers to stricturing behaviour, and B3 to penetrating behaviour. (A) includes 35 patients with Crohn’s disease who either developed complications during the first 90 days after diagnosis, or did not have complete information for disease location at diagnosis, and were therefore excluded from the primary analysis. 97 patients developed complications, 63 with stricturing behaviour and 34 with penetrating behaviour. In (B), early anti-TNFα therapy was defined as exposure within 90 days of diagnosis, and the survival probabilities were computed among those staying complication free by 90 days. Among those treated with early anti-TNFα therapy, 18 patients developed complications, 14 with stricturing behaviour and four with penetrating behaviour. 23 patients developed complications, 12 with stricturing behaviour and 11 with penetrating behaviour, among the matched group not treated with early anti-TNFα therapy. TNFα=tumour necrosis factor α.