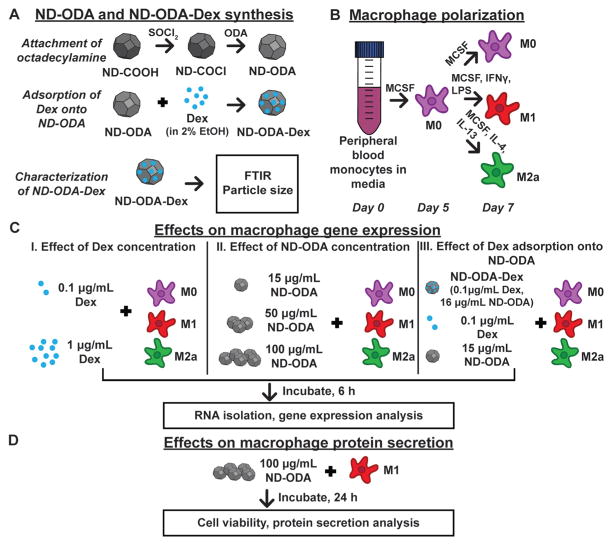
Fig. 1.
Overview of the experimental design. (A) ND-ODA was synthesized by first chlorinating carboxylated ND, and then replacing the active chlorine group with ODA. Then, Dex was adsorbed onto ND-ODA. The ND-ODA-Dex complexes were then further characterized by FTIR and particle size analysis. (B) Peripheral blood monocytes were differentiated into M0 macrophages. At day 5, the cells were either kept as M0 or further polarized into M1 and M2a phenotypes in ultra-low attachment well-plates. (C) After polarization was complete at day 7, either Dex (at low and high concentrations), ND-ODA (at low, medium, or high concentrations), or Dex-loaded (ND-ODA-Dex; at low Dex and low ND concentrations) was added to cells and incubated for 6 h prior to RNA isolation and gene expression analysis. (D) To confirm the gene expression data on the protein level, the high dose of ND-ODA was incubated with M1 macrophages for 24 h. Then, the cells were counted and the conditioned media was analysed for protein secretion.