Fig. 1.
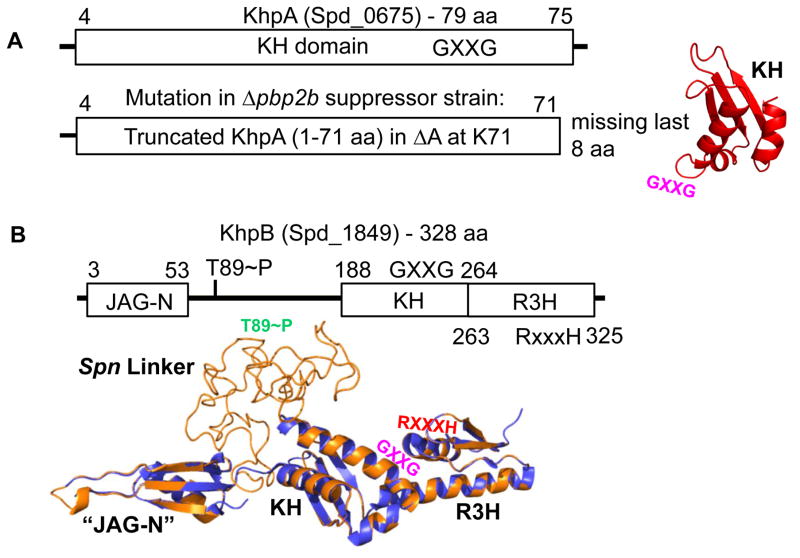
Domain and modeled structures of KhpA (Spd_0675) and KhpB (Spd_1849) (not drawn to scale). A. KhpA contains only one KH (“K Homology”) RNA-binding domain (amino acids (aa) 4–75). Truncated KhpA in the original D39 Δcps Δpbp2b sup1 suppressor strain (Table S2) is indicated. The structure of KhpA was modeled as described in Experimental procedures. The location of the GXXG motif in KhpA is indicated. B. KhpB contains a Jag-N domain of unknown function, KH and R3H (“RXXXH”) RNA-binding domains. KhpB is phosphorylated by StkP at T89 and one other residue (Stamsas et al., 2017, Ulrych et al., 2016). KhpB structure (tan) was modeled on the known structure of the KhpB homologue of Clostridium symbiosum (purple), which lacks a large linker region between its JAG-N and KH domains. The large linker region of Spn KhpB, which contains phosphorylated T89, lacks predicted domains, and its structure is unknown. The locations of the GXXG (KH) and RXXXH (R3H) motifs and T89~P (Spn Linker) are marked.