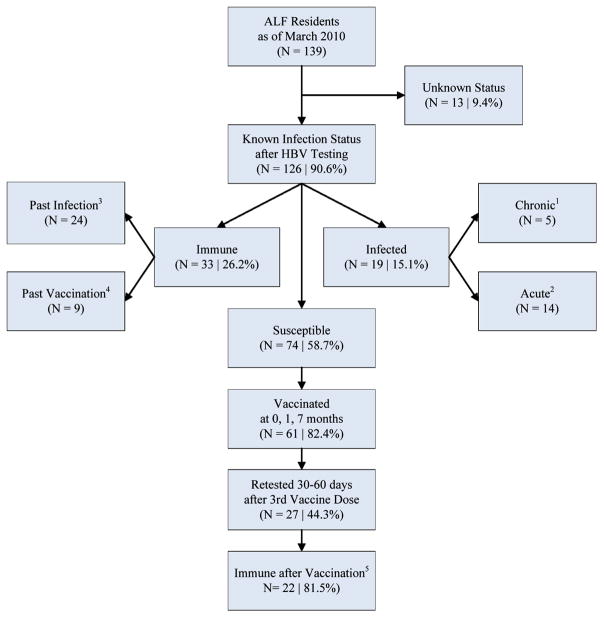
Fig. 1.
Participant flow chart for hepatitis B screening and vaccination—Virginia, 2010. ALF, assisted living facility; HBV, hepatitis B virus; anti-HBs, antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen; anti-HBc, antibody to hepatitis B core antigen; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; immune, anti-HBs ≥10 mIU/mL. 1 Serologic markers indicating chronic infection: positive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and total hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc), negative hepatitis B IgM core antibody (IgM anti-HBc). 2 Serologic markers indicating acute infection: positive HBsAg and IgM anti-HBc. One resident was determined to have acute infection based on a well-documented HBsAg seroconversion even though IgM-anti-HBc remained negative. 3 Serologic markers indicating immunity to hepatitis B due to past infection: positive hepatitis B antibody to surface antigen (anti-HBs) and total hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc). 4 Serologic markers indicating immunity to hepatitis B due to past vaccination: positive anti-HBs (level ≥10 mIU/mL) and anti-HBc negative. 5 Seroprotective response defined as anti-HBs ≥10 mIU/mL.