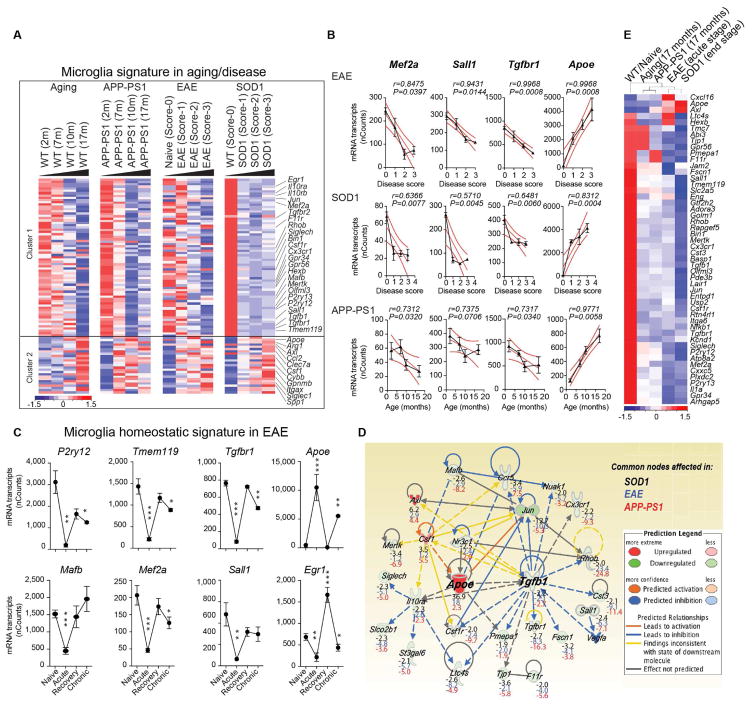
Figure 1. Reciprocal induction of APOE and suppression of TGFβ signaling in disease-associated MGnD-microglia.
(A) K-means clustering of 95 significantly affected common genes in FCRLS+ microglia during aging and disease by Nanostring). Vertical lanes are biological replicates per disease stage/condition in WT-aging (n = 12), EAE (n = 18), SOD1 (n = 11) and APP-PS1 (n = 12) mice. Cluster 1: suppressed homeostatic genes; cluster 2: upregulated genes.
(B) Linear regression curve of Mef2a, Sall1, Tgfbr1 and Apoe in EAE (n = 4–6 mice/disease score) and SOD1 (n = 2–4 mice/disease score) spinal cord microglia and APP-PS1 (n = 3 mice/age) brain microglia. Thick line: 95% confidence interval of the regression line.
(C) Selected homeostatic and disease-associated microglial genes during EAE (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison post-hoc test.
(D) IPA shows common nodes significantly affected in microglia in all three-mouse models in disease. For each molecule, the expression fold change compared to normal, homeostatic microglia is presented.
(E) Heatmap of significantly affected genes dysregulated in all 3 diseases (n = 3–4) determined by Nanostring. Vertical lanes: mean of biological replicates per disease stage/condition as indicated in (A).