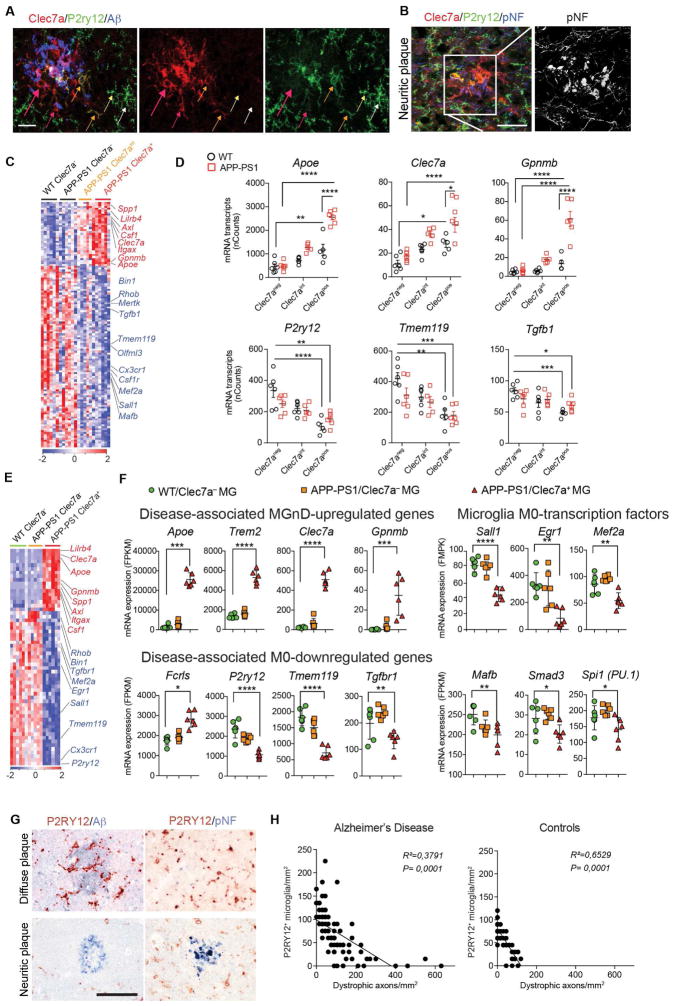
Figure 2. MGnD-microglia are associated with neuritic Aβ-plaques.
(A) Staining for P2ry12+ and Clec7a+ in Aβ-plaque microglia in 24-month-old APP-PS1 mice. MGnD around plaque (red arrows). MGnD transitioning to plaque (yellow arrows). M0-homeostatic microglia (white arrows). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Staining for P2ry12+ and Clec7a+ in microglia associated with neuritic plaque (pNF) in APP-PS1 mice (24 month). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(C) Heatmap of significantly affected genes in Clec7a+ vs. Clec7aint vs. Clec7a− FCRLS+ microglia in APP-PS1 vs. WT mice (n = 5; 24 month). Selected homeostatic (blue) and inflammatory (red) genes.
(D) Selected genes shown in (C). Dot plots: mRNAs transcripts (mean ± s.e.m). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p< 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison post-hoc test.
(E) Heatmap of significantly affected genes determined by RNAseq in Clec7a+ vs. Clec7a− FCRLS+ microglia in APP-PS1 vs. WT mice (n = 5; 9 month).
(F) Selected genes shown in (E). Dot plots: FPKM (mean ± s.e.m). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p< 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison post-hoc test.
(G) Staining for P2RY12 with Aβ or pNF in diffuse vs. neuritic plaques in human AD brain. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(H) Linear regression curve of P2RY12+ microglia with dystrophic axons in control temporal cortex and AD defined by CERAD criteria and Braak stages (n = 14) and age-matched controls (n = 10).