Figure 3. Progression stages of growth of a bacterial biofilm.
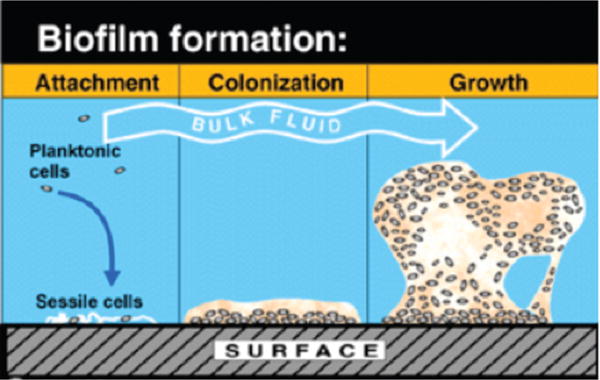
Initially free-floating planktonic cells settle down onto a surface that can either be inanimate or living tissue. Next secretion of extracellular matrix allows the cells to grow in place. Finally, a mature biofilm is formed complete with water channels to allow oxygen and nutrients to penetrate.
