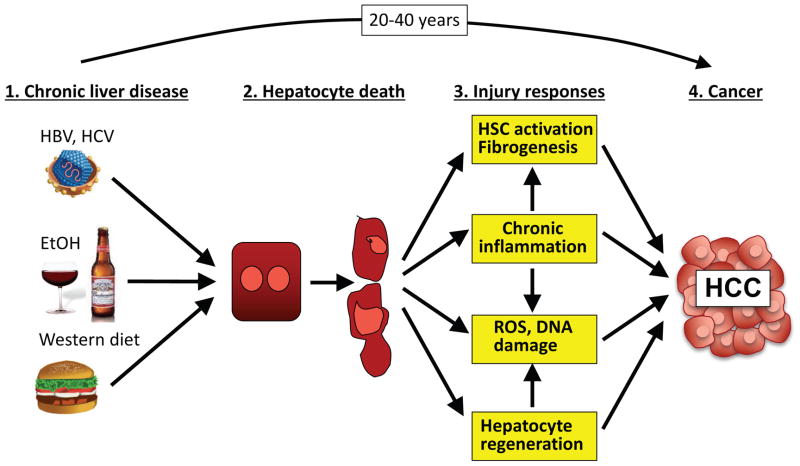
Figure 1. Mechanisms by which the hepatic PME promotes HCC development.
Chronic liver injury, resulting in hepatocyte death, contributes to characteristic features of the PME, including liver fibrosis, hepatocyte regeneration, inflammation, increased generation of ROS, and DNA damage. Together these changes in the PME drive the development of HCC, which typically occurs after chronic injury persists for several decades. Abbreviations: HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; PME, premalignant environment; ROS, reactive oxygen species.