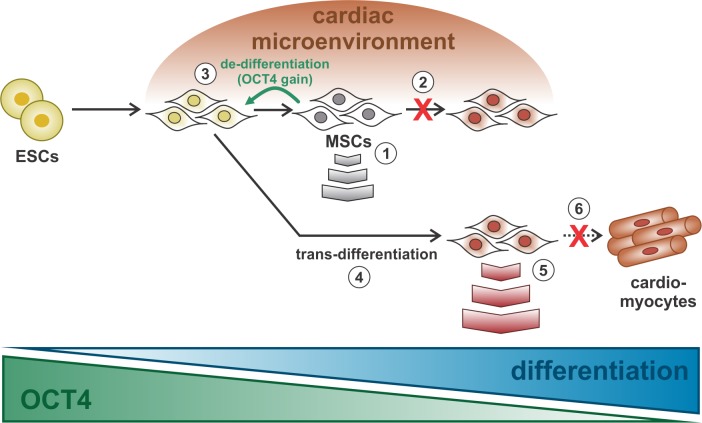
Fig 6. OCT4 expression is required for interaction of MSCs with the cardiac microenvironment.
A schematic depicting the main mechanisms proposed in the present study. (1) MSCs have a basal expression of OCT4 and release several growth factors and cytokines under normal conditions. (2) MSCs interact with the cardiac microenvironment and partially differentiate into cardiomyocytes, by an indirect mechanism. (3) As a result of the interaction with the cardiac microenvironment, MSCs de-differentiate with a net gain in OCT4 expression. (4) De-differentiated MSCs express higher levels of OCT4 and can start the differentiation process into cardiomyocytes. (5) MSCs acquire a partial cardiomyocyte phenotype that modulates the paracrine effect and improves their cardiac regenerative potential. (6) Full cardiomyocyte differentiation of MSCs to generate completely mature cardiomyocytes was not observed. Abbreviations: ESC, embryonic stem cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells.