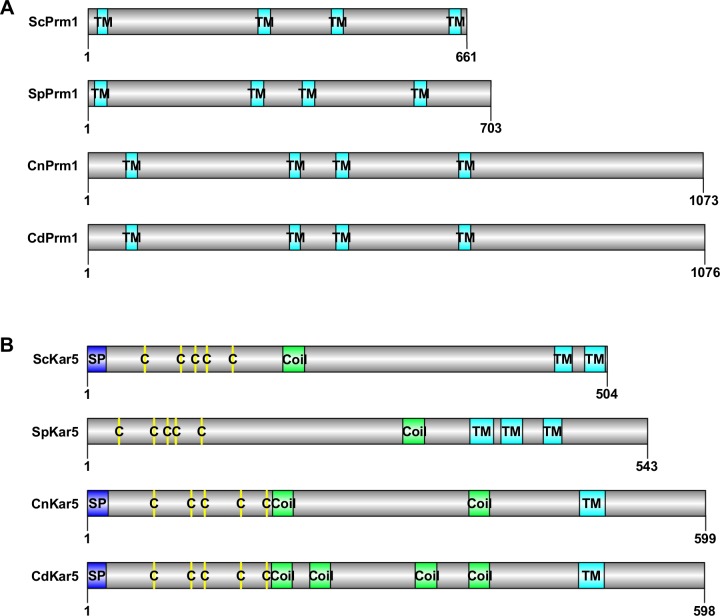
Fig 1. Schematic diagrams of Cryptococcus Prm1 and Kar5 proteins.
(A) The Prm1 proteins from S. cerevisiae, S. pombe, C. neoformans, and C. deneoformans are drawn to scale. The four Prm1 proteins contain four transmembrane domains (TM) indicated by cyan boxes. In contrast to ScPrm1 and SpPrm1, CnPrm1 and CdPrm1 have a long C-terminal tail following the last transmembrane domain. (B) The Kar5 proteins from S. cerevisiae, S. pombe, C. neoformans, and C. deneoformans are drawn to scale. CnKar5 and CdKar5 protein domain structures are conserved with ScKar5 and SpKar5. All four proteins contain a cysteine-rich domain (C) indicated by yellow lines, a coiled-coil domain (Coil) indicated by green boxes, and C-terminal transmembrane domains (TM) indicated by cyan boxes. ScKar5, CnKar5, and CdKar5 contain an N-terminal signal peptide (SP) indicated by a blue box.