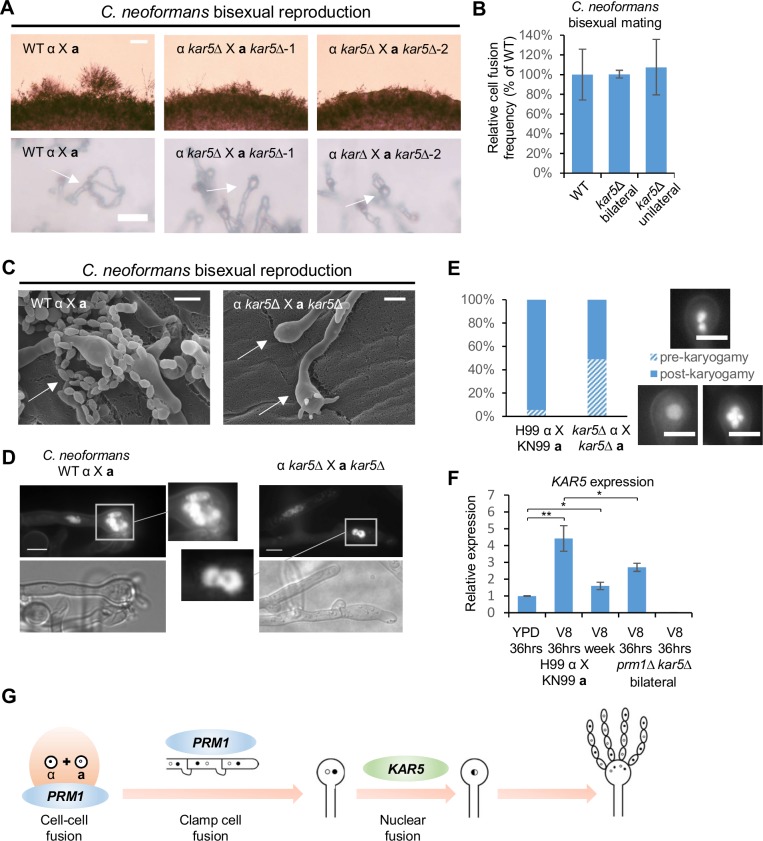
Fig 3. Deletion of KAR5 causes a sporulation defect during C. neoformans bisexual reproduction.
(A) Mating phenotypes for a wild type cross between H99α and KN99a and two independent kar5 bilateral mutant crosses between CF57 and CF549, and CF208 and CF305. The scale bars are 100 μm and 20 μm for top row and bottom row, respectively. (B) Unilateral and bilateral kar5 mutant cell fusion frequency compared to wild type. (C) Scanning electron microscopy of basidium morphology and sporulation patterns (indicated by arrows) for wild type cross (H99α X KN99a) and kar5 bilateral mutant cross (CF57 X CF549). The scale bar is 5 μm. (D) DAPI staining of nuclei inside basidia from C. neoformans wild type (left panel) and kar5 mutant (right panel) bisexual crosses. Basidia indicated by white boxes were magnified to show nuclei morphology. The scale bar is 5 μm. (E) Quantification of pre-karyogamy and post-karyogamy events for wild type and kar5 mutant crosses based on DAPI staining of nuclei inside basidia. Representative pre-karyogamy (two nuclei) and post-karyogamy (one nucleus and post meiosis) events were shown on the right. The scale bar is 5 μm. (F) Gene expression patterns for KAR5 were examined by RT-PCR (* indicates p <0.05 and ** indicates p <0.005 for each pairwise comparison). Wild type cross (H99α X KN99a) was grown on YPD medium for 36 hours, and on V8 medium for 36 hours or one week. prm1 bilateral mutant cross (CF56 X CF562) and kar5 bilateral mutant cross (CF57 X CF549) were grown on V8 medium for 36 hours. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean for the three biological replicates. (G) Proposed C. neoformans bisexual reproduction model. PRM1 is required for cell-cell fusion and clamp cell fusion, and KAR5 is required for karyogamy inside the basidium.