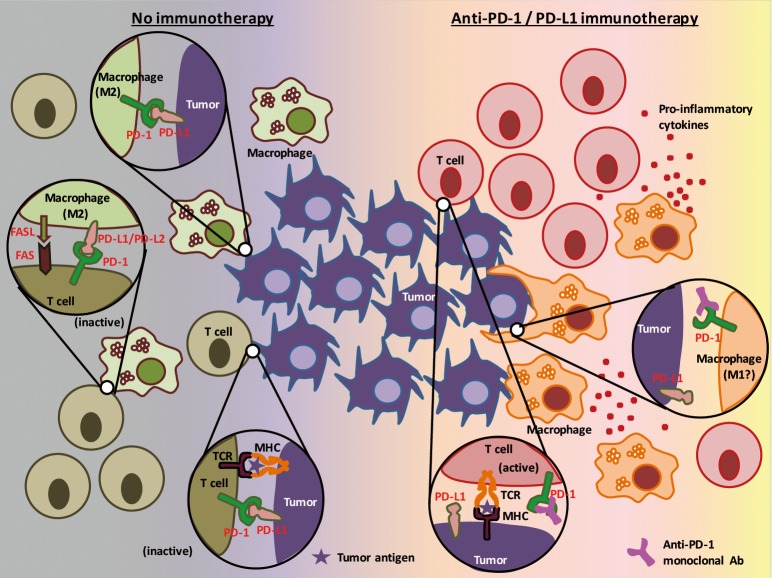
Figure 2.
Model of action of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy focusing on tumor cells, cytotoxic T cells, and tumor associated macrophages (TAMs). PD-1 is expressed not only in T cells, but also in TAMs, leading these cells to become inactivated upon binding to PD-L1 expressed on tumor cells. TAMs (M2 TAMs) also express PD-L1 and the ligand for the death receptor FAS that inactivates T cells and triggers caspase-dependent cell death in T cells, respectively (left). Treatment with an anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody drug not only activates cytotoxic T cells, but also affects TAMs so that they increase phagocytic potency against tumor cells (right).