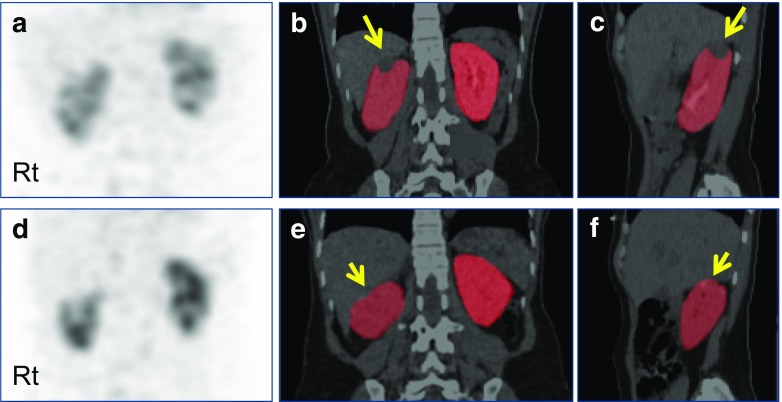
Fig. 5.
Quantitative SPECT/CT for perioperative GFR assessment in a patient with a renal tumor. The 45-year-old female patient had a renal cell carcinoma in the upper pole of the right kidney (long arrows, b and c). The right kidney was subjected to robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, and postoperative quantitative SPECT/CT was acquired 3 months after surgery (resection site is highlighted by short arrows, e and f). Compared with the preoperative quantitative SPECT/CT, the postoperative quantitative SPECT/CT showed a substantial change in GFR in the nephrectomized right kidney from 56.61 ml/min to 48.48 ml/min. On the other hand, the contralateral left kidney exhibited similar single kidney GFR values before (58.34 ml/min) and after surgery (61.08 ml/min). (a) Preoperative maximum-intensity projection (MIP) anterior image; (b) preoperative coronal SPECT/CT image with kidney segmentation; (c) preoperative sagittal SPECT/CT image with kidney segmentation showing right kidney; (d) postoperative MIP anterior image; (e) postoperative coronal SPECT/CT image with kidney segmentation; (f) postoperative sagittal SPECT/CT image with kidney segmentation showing right kidney