Figure 1.
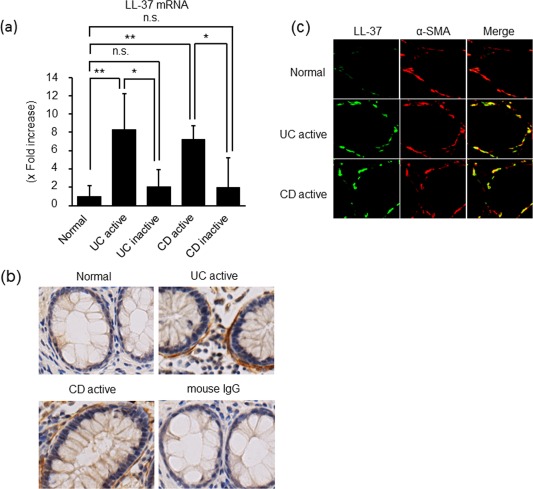
LL‐37 expression in the inflamed mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). (a) The mRNA expression of LL‐37 in the inflamed mucosa of patients with IBD. Total RNA was extracted from biopsied samples, and the mRNA expression of LL‐37 was evaluated using real‐time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). LL‐37 mRNA expression was converted to a value relative to β‐actin mRNA expression, and presented as an increase relative to normal mucosa. Data are expressed as mean values ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). Normal mucosa, n = 20; active ulcerative colitis (UC), n = 23; inactive UC, n = 27; active Crohn's disease (CD), n = 20; inactive CD, n = 20. **P < 0·01, *P < 0·05; not significant (n.s.). (b) Immunostaining for LL‐37 in normal mucosa and inflamed mucosa of UC and CD. Normal mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)G was used as the primary antibody for active UC samples. Pictures are shown from one of six independent samples with similar results. Magnification ×200. (c) Dual‐coloured immunofluorescence was used to determine expression of LL‐37 (green fluorescence) and α‐smooth muscle actin (SMA) (red fluorescence) in the inflamed mucosa of patients with UC and CD. Representative pictures are shown from one of six independent samples. Double‐positive cells were detected by yellow fluorescence. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
