Figure 2.
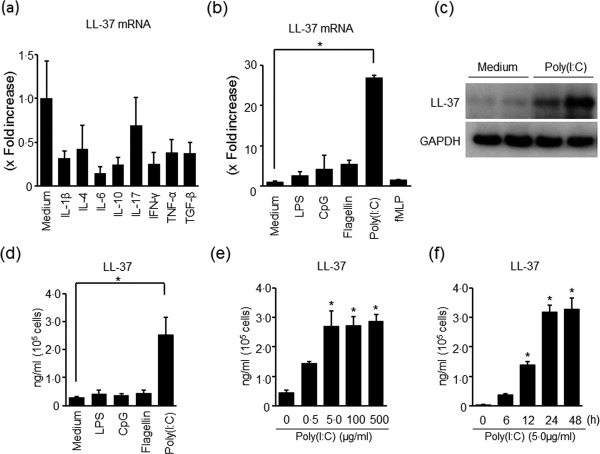
LL‐37 expression in colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts (SEMFs). (a) The expression of LL‐37 mRNA in response to cytokines. The cells were stimulated for 12 h with cytokines [interleukin (IL)‐1β: 10 ng/ml, IL‐4: 100 ng/ml, IL‐6: 100 ng/ml, IL‐10: 100 ng/ml, IL‐17: 100 ng/ml, interferon (IFN)‐γ: 100 ng/ml, TNF‐α: 100 ng/ml and transforming growth factor (TGF)‐β: 100 ng/ml], and the mRNA expression of LL‐37 was determined using real‐time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). LL‐37 mRNA expression was converted to a value relative to β‐actin mRNA expression, and presented as fold increase relative to the results for medium alone (no stimulation). Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) of four independent experiments. (b) The expression of LL‐37 mRNA in response to Toll‐like receptor (TLR) ligands and N‐formyl‐L‐methionyl‐L‐leucyl‐phenylalanine (fMLP). The cells were stimulated for 12 h with TLR ligands [poly(I:C)]: 5 µg/ml, lipopolysaccharide (LPS): 100 ng/ml, fragellin: 5 µg/ml and cytosine–phosphate–guanosine (CpG): 1 µg/ml) and N‐formyl‐L‐methionyl‐L‐leucyl‐phenylalanine (fMLP) (100 nM), and the mRNA expression of LL‐37 was determined using real‐time PCR. LL‐37 mRNA expression was converted to a value relative to β‐actin mRNA expression, and presented as fold increase relative to the results for medium alone (no stimulation). Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05. (c) The expression of LL‐37 protein in response to poly(I:C) stimulation. The cells were stimulated for 24 h with 5 µg/ml of poly(I:C), and the expression of LL‐37 protein in the cells was evaluated using immunoblot analysis. The expression of glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) used as a loading control is shown. The data are representative of two independent experiments. (d) The secretion of LL‐37 protein in response to poly(I:C) stimulation. The cells were stimulated for 24 h with 5 µg/ml of poly(I:C), and the level of LL‐37 in the supernatants was determined using enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05. (e) Dose‐dependent effects of poly(I:C) on LL‐37 secretion. The cells were stimulated for 24 h with increasing concentrations of poly(I:C), and the level of LL‐37 in the supernatants was determined using ELISA. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05. (f) The kinetics of LL‐37 secretion in response to poly(I:C) stimulation. The cells were stimulated with 5 µg/ml of poly(I:C) for the indicated predetermined times, and LL‐37 levels in the supernatant were determined using ELISA. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05.
