Figure 5.
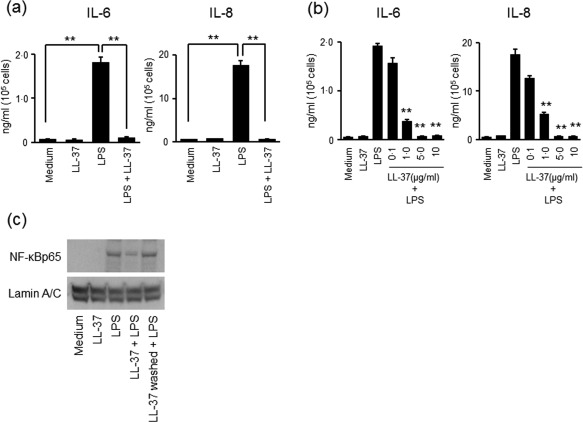
The effect of LL‐37 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐induced expression of interleukin (IL)‐6 and IL‐8. (a) The effect of LL‐37 on LPS‐induced expression of IL‐6 and IL‐8. The cells were incubated for 24 h with or without LL‐37 (5·0 µg/ml), LPS (100 ng/ml) or LL‐37 (5·0 µg/ml) plus LPS (100 ng/ml). The levels of IL‐6 and IL‐8 in the supernatants were measured using enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) of four independent experiments. **P < 0·01. (b) Dose‐dependent effects of LL‐37 on LPS‐induced secretion of IL‐6 and IL‐8. The cells were incubated for 24 h with a combination of LPS (100 ng/ml) and increasing concentrations of LL‐37. The levels of IL‐6 and IL‐8 in the supernatants were measured using ELISA. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. **P < 0·01. (c) The effect of LL‐37 on LPS‐induced translocation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF‐κB)p65 into the nucleus. The cells were incubated for 15 min with medium alone, LL‐37 (5·0 µg/ml), LPS (100 ng/ml) or LL‐37 (5·0 µg/ml) plus LPS (100 ng/ml). Another group of cells was pretreated with LL‐37 (5·0 µg/ml) for 1h and then washed with phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS), and then LPS (100 ng/ml) was added and incubated for 15 min. NF‐κBp65 in the nuclear protein was analysed using immunoblotting. The data are representative of two independent experiments.
