Figure 3.
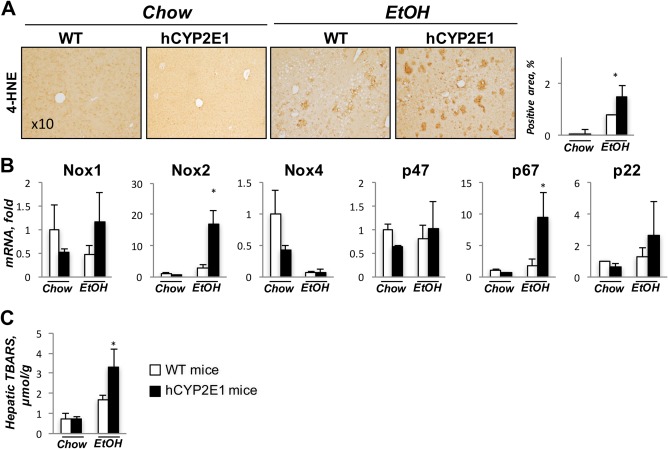
Alcohol‐induced oxidative stress is increased in hCYP2E1 compared to Wt mice. CYP2E1‐induced oxidative stress during alcohol consumption is a major pathology during alcoholic liver disease. (A) Representative images of immunohistochemistry staining of 4‐HNE are shown with quantification of the positive area. (B) Liver mRNA of ROS production genes was measured in Wt and hCYP2E1 mice after iG alcohol feeding. (C) Hepatic lipid peroxidation was assessed by measuring TBARS formation. The data are shown as the fold change of mRNA induction compared with Wt chow mice. The P value was measured between Wt and hCYP2E1 under iG alcohol feeding; the data were shown as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05. Abbreviations: EtOH, ethanol; iG, intragastric; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances.
