Figure 4.
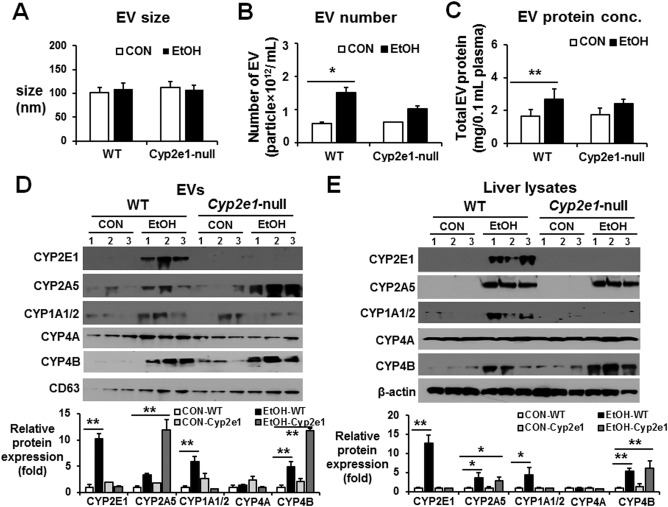
CYP2E1 deletion prevented alcohol‐medicated increments of hepatic P450 proteins and the amounts of total EV proteins and P450 isoforms in mice. WT or Cyp2e1‐null mice were exposed to dextrose (CON) or 6 g ethanol/kg/dose via oral gavage 3 times at 12‐hour intervals and were sacrificed 1 hour after the third dose (n = 7/group). (A) Analysis of the size of circulating EVs isolated from each group. (B) Total number of EVs in each group was measured by Nanosight. (C) Analysis of the protein amounts in circulating EVs isolated from each group, as indicated. (D) Detection of the P450 proteins (e.g., CYP2E1, CYP2A5, CYP1A1/2, CYP4A, and CYP4B) in circulating EVs from the different groups by immunoblot analyses, as indicated. Densitometric quantitation of the immunoblots for EV CYP proteins relative to CD63, used as a loading control, is shown. (E) Detection of the hepatic P450 isoforms from the different groups by immunoblot analyses, as indicated. Densitometric quantitation of the immunoblots for hepatic CYP proteins relative to β‐actin, used as a loading control, is shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Abbreviations: CON, control; EtOH, ethanol. Data are shown as means ± SD.
