Figure 3.
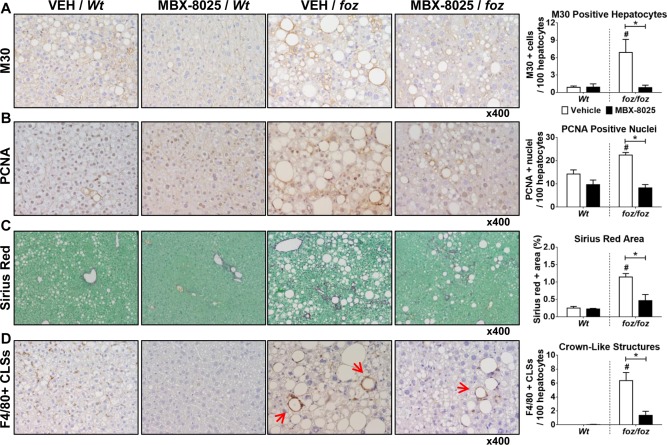
Effects of MBX‐8025 on hepatocyte apoptosis, proliferation, fibrosis, and liver inflammation in atherogenic diet–fed foz/foz and Wt mice. (A) As quantified by cytokeratin‐18 fragmentation (M30) immunohistochemistry, vehicle‐treated foz/foz mouse livers showed more hepatocytes undergoing apoptosis than Wt; MBX‐8025 normalized this to Wt levels. (B) The number of PCNA–positive liver cells, reflecting hepatocytes in the cell cycle, was higher in vehicle‐treated foz/foz mice than Wt; and MBX‐8025 lowered this value after 8 weeks of treatment. (C) Densitometry of collagen+ areas by sirius red staining showed that Wt mice developed very mild fibrosis after 24 weeks of atherogenic dietary feeding, so MBX‐8025 could not affect liver fibrosis in these mice. foz/foz mice developed significant fibrosis, and MBX‐8025 treatment reduced collagen density in these mice. (D) Macrophage CLSs around injured hepatocytes (arrows) were abundant in livers of vehicle‐treated foz/foz, but not Wt, mice; MBX‐8025 reduced the number of hepatic CLSs in these mice. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 8‐12 per group). * P < 0.05 compared with genotype‐matched control (MBX‐8025 effect). # P < 0.05 compared with treatment‐matched control (genotype effect). Abbreviations: CLS, crown‐like structure; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; VEH, vehicle.
