Fig. 4.
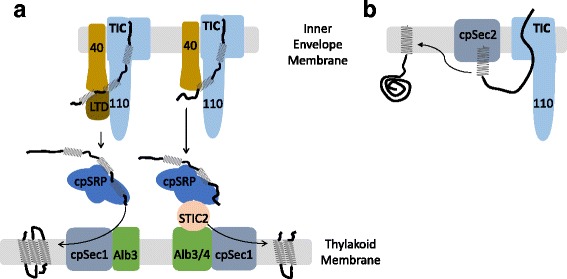
The TIC complex interacts with factors that facilitate the targeting of proteins to the inner envelope and thylakoid membranes to avoid potential mis-sorting of hydrophobic membrane proteins to the stroma. a At least five mechanisms conserved from the original bacterial endosymbiont exist for targeting proteins to the internal thylakoids of chloroplasts. The cpSRP system mediates the targeting of abundant thylakoid membrane proteins, including the light harvesting complex proteins. Genetic and biochemical evidence has identified a novel factor, LHCP translocation defect (LTD) protein, that docks at the inner membrane via an interaction with TIC components, Tic40 and Tic110, and also binds to cpSRP. LTD is proposed to facilitate the passage of LHCP proteins from the import apparatus to the cpSRP4 for delivery to the thylakoid Sec translocase (cpSec1). In a related pathway, Albino4 (ALB4), a homologue of ALB3, and STIC2, a homologue of bacterial YbaB, function by linking TIC and cpSRP to facilitate the targeting of a subset of proteins other than LHCPs to the thylakoid membrane. b Inner envelope membrane proteins are integrated into the membrane by a stop-transfer mechanism directly via the TIC channel or following import via a cpSec2 system (post-import/conservative mechanism) that catalyzes membrane protein integration from the stroma. For proteins using the post-import/conservative mechanism, the TIC complex and the cpSec2 system cooperate to allow protein import and membrane integration to proceed simultaneously to facilitate targeting to the inner membrane
