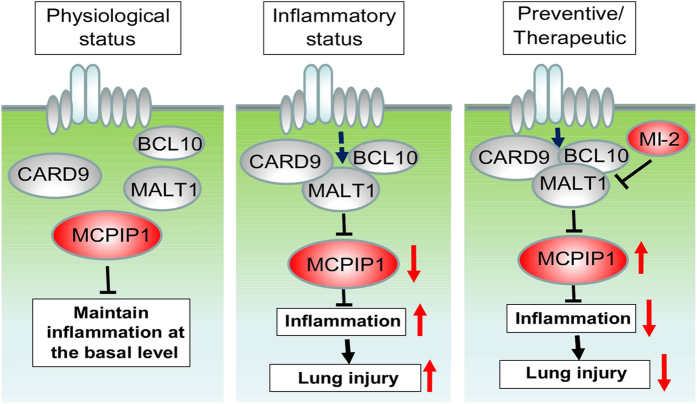
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the central role of MCPIP1 in LPS-induced inflammation and lung injury. As an RNase, MCPIP1 post-transcriptionally controls the production of cytokines and maintains inflammation at a basal level under physiological conditions. In response to inflammatory stimuli (for example, LPS), macrophage CARD9/BCL10/MALT1 signalosome is activated and MALT1 protease mediates MCPIP1 cleavage, which releases the ‘brake’ and initiates the inflammatory response. MI-2 specifically inhibits MALT1 protease activity and preserves the MCPIP1 protein levels, which can prevent/treat LPS-induced inflammation and lung injury.