Fig. 4.
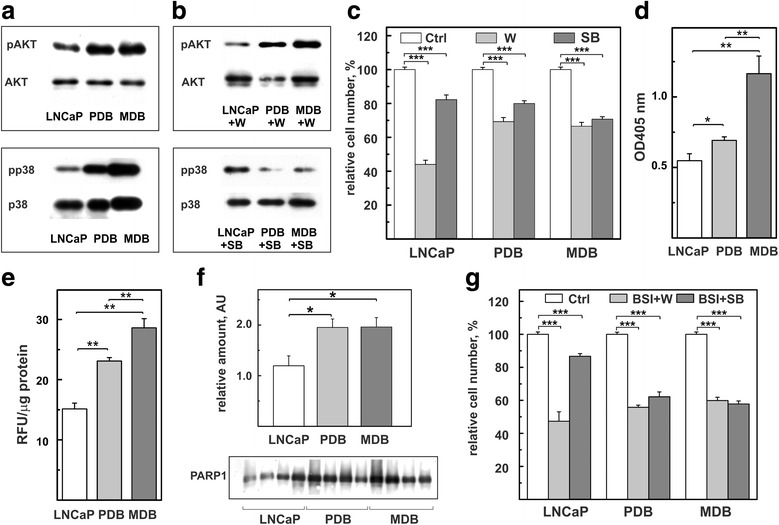
Prolonged BIC exposure activates non-androgen signaling pathways and enhances apoptosis, ROS levels and PARP-1 expression. Representative WB analysis of total proteins extracted from LNCaP, PDB and MDB untreated (a) or treated for 72 h (b) with 1 μM wortmannin (W, top panel) or 1 μM SB203580 (SB, bottom panel) and probed with antibodies against AKT, ppAKT, p38MAPK and pp38MAPK. One experiment, out of two with similar results, is reported. c LNCaP, PDB and MDB were treated with 1 μM W or 1 μM SB for 120 h. d Basal levels of apoptosis measured as cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments. Values are representative of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Mean ± SE are reported. e Intracellular ROS quantified by fluorimetry as reported in materials and methods. Values are representative of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Mean ± SE are reported. f WB analysis of PARP-1 expression in four different preparations. Histogram represents the mean ± SE of the relative amounts of the proteins determined by quantitative analysis of WB. g Viability of LNCaP, PDB and MDB cells co-treated for 120 h with 10 μM BSI-201 in the presence of 1 μM W or 1 μM SB. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001
