Fig. 1.
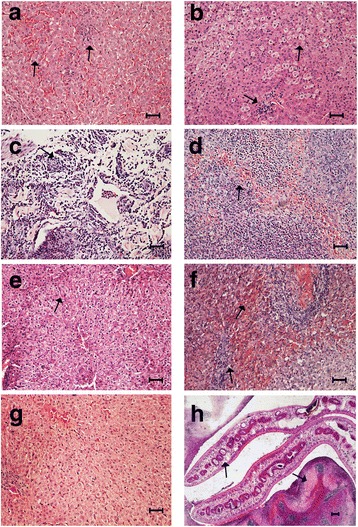
Histopathological characteristics of the livers of buffaloes infected with Fasciola gigantica. a At 3 dpi, there was local hyperemia associated with mild filtration of lymphocytes and neutrophils. b At 10 dpi, there was scattered vacuolation of hepatocytes, consistent with fat, along with mild to moderate focal necrosis. c At 28 dpi, diffuse intravascular coagulation, severe infiltration of inflammatory cells mainly neutrophils and lymphocytes, and granular degeneration of the cytoplasm were observed. d At 42 dpi, moderate to severe multifocal hemorrhages and necrosis, infiltration of eosinophils, RBCs and monocytes, and accumulation of fibroblasts were detected. e At 70 dpi, there were mild to moderate multifocal bile duct hyperplasia and focal coagulative necrosis associated with collagen deposition. f At 98 dpi, severe periportal fibrosis associated with multifocal inflammatory infiltrate, cellular debris, moderate multifocal hemorrhages, and granulomas with necrotic centres were detected. g Liver tissue from uninfected animal showed normal histological architecture of the hepatic tissue. h Adult flukes in the intrahepatic bile duct, along with epithelial hyperplasia of the duct. In all figures, tissue sections were stained with H&E and arrows point at the corresponding morphological features described above. Scale-bars: a-g, 50 μm; h, 100 μm
