Fig. 3. Fgd5+ HSCs generate a microglia-like progeny in the brain upon both intracerebroventricular and intravenous transplantation.
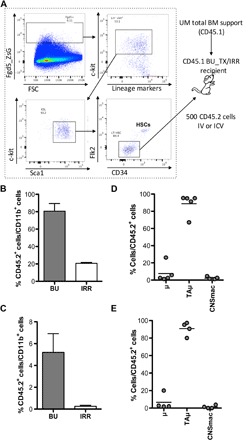
(A) Experimental scheme. Fgd5+ HSCs (Lin− ckit+ Sca-1+ Flk2− CD34−) were isolated from CD45.2 Fdg5-green donor mice. Five hundred Fgd5+ HSCs were transplanted intravenously or intracerebroventricularly into BU-myeloablated or lethally IRR CD45.1 recipient mice. Transplanted animals also received UM CD45.1 total BM cells for hematopoietic rescue at day 5 after transplant. FSC, forward side scatter. (B and C) Frequency of donor cells (CD45.2+) within brain myeloid CD11b+ cells of mice transplanted intravenously (B) and intracerebroventricularly (C) with Fgd5 cells after BU and irradiation conditioning. n ≥ 4 per group. (D and E) Frequency of μ, TAμ, and CNSmac populations within donor-derived cells in intravenously (D) and intracerebroventricularly (E) transplanted BU-conditioned mice. n ≥ 4 per group; average and SD are shown. Student’s t test, P < 0.001 for BU versus irradiation in (B) and (C).
