Figure 3.
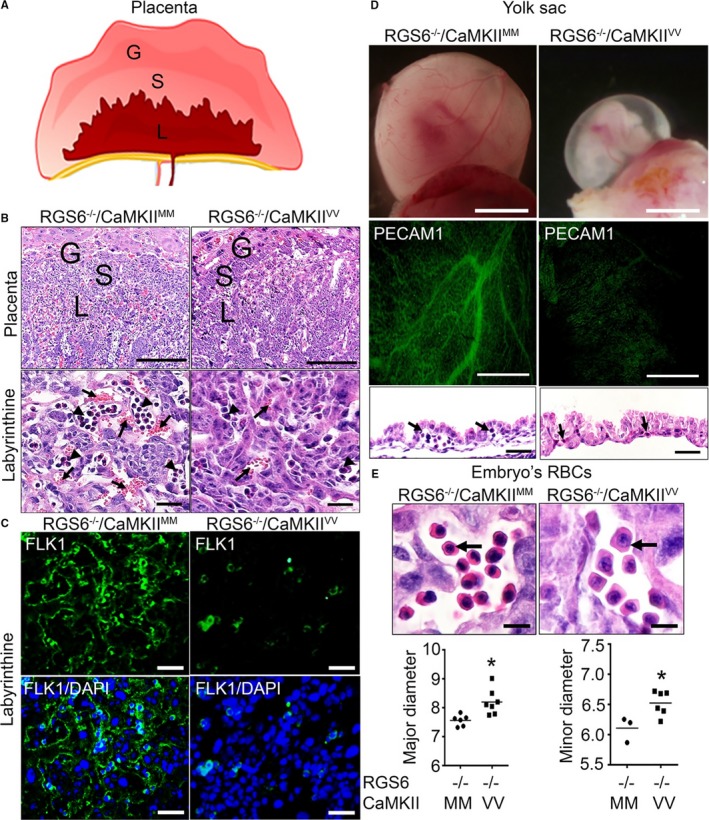
Vascular remodeling and hematopoietic defects in Regulator of G protein signaling 6 (RGS6)−/−/Ca2+/calmodulin‐dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)VV placentas, yolk sacs, and embryos. A, Schematic representation of different layers of placenta in mice; giant (G), spongiotrophoblast (S), and labyrinthine (L) layers. B, Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM and RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV placenta illustrating G, S, and L layers. Higher magnification images of the labyrinthine layer reveals reduced maternal and fetal blood–filled vasculature in RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV placentas. Arrows indicate maternal blood (anucleated) and arrowheads indicate fetal blood (nucleated). Scale bars=200 μm (placenta) and 5 μm (L). C, Fetal liver kinase 1 immunostaining of the placental L region revealed a reduction in embryonic vessels in RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV placentas compared with RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM placentas. Scale bars=50 μm. D, Representative images of embryos within their yolk sacs show what appears to be an absence of blood‐filled large vitelline vessels, which we later confirmed using whole‐mount platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM1) immunostaining. H&E staining of yolk sacs section reveals fewer blood/hematopoietic cells in vessels (black arrows) in RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV yolk sacs at E10.5 compared with RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM yolk sacs, suggesting altered vascular remodeling and hematopoiesis from blood islands. Scale bars=200 μm (whole‐mount and PECAM1) and 20 μm (yolk sac), and (E) larger red blood cell (RBC) nuclei and cell sizes were observed in RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV embryo sections. Scale bar=20 μm. Both the major and minor diameter of RBCs were significantly larger in RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV embryos compared with RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM embryos analyzed by Mann–Whitney statistical methods. N=3, *P<0.05. DAPI indicates 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole.
