Figure 7.
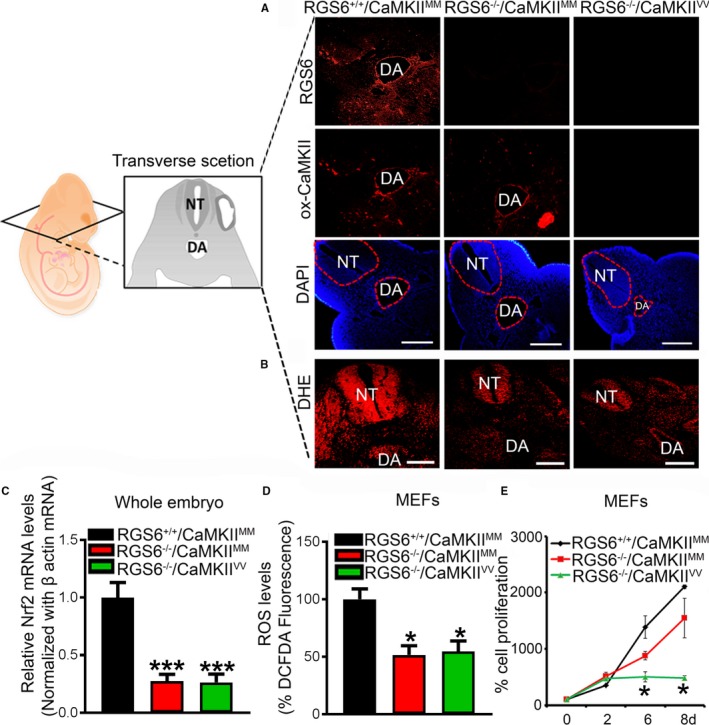
Regulator of G protein signaling 6 (RGS6), oxidized Ca2+/calmodulin‐dependent protein kinase II (ox‐CaMKII), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) expression in embryos of different genotypes. A, Detection of RGS6 (red) and ox‐CaMKII (red) levels in wild‐type (RGS6+/+/CaMKIIMM), RGS6−/− (RGS6−/−/Ca2+/calmodulin‐dependent protein kinase II [CaMKII]MM), and RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV double mutant embryos by immunostaining. Scale bars=50 μm. B, Effects of combined loss of RGS6 and ox‐CaMKII on superoxide (red) generation in the head region of embryos as shown by dihydroethidium (DHE) staining. The transverse sectioning plane of embryos is represented in the schematic diagram. Scale bars=50 μm. C, Relative Nrf2 mRNA expression levels were analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction in RGS6+/+/CaMKIIMM, RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM, and RGS6−/−/CaMKIIVV embryos. D, ROS levels in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) using 2′,7′‐dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate fluorescence. E, Cell proliferation of MEFs at different days using MTT assay. N=3. *P<0.05, ***P<0.01 RGS6−/−/CaMKIIMM or RGS6−/− CaMKIIVV vs RGS6+/+/CaMKIIMM. DA indicates dorsal aorta; DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; NT, neural tube.
