Figure 3.
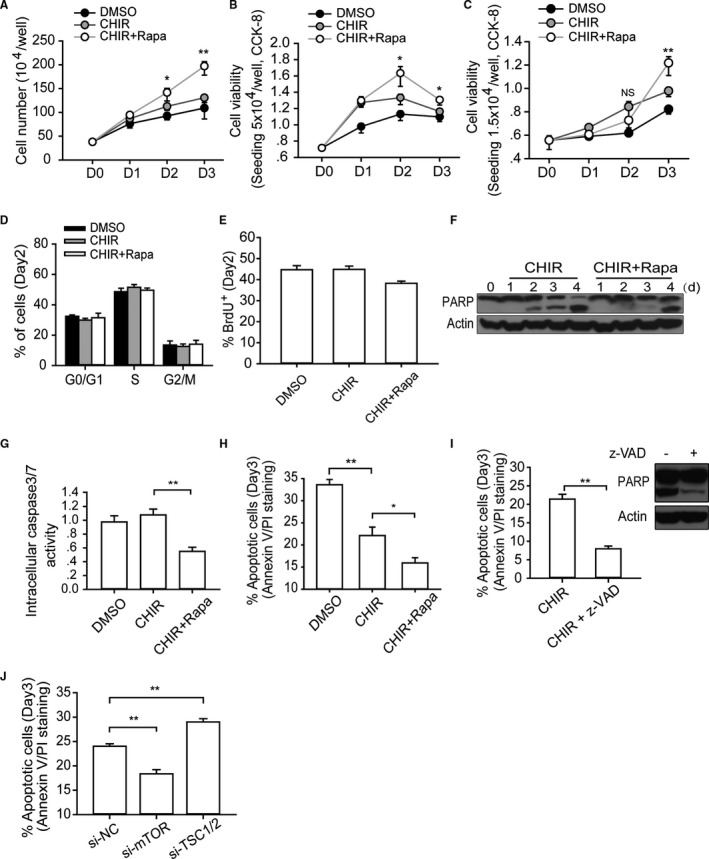
mTOR regulates the apoptosis of hESCs during high‐density monolayer culture. A and B, Cell number calculation and viability measurement. Single H9 cells (5×104/well) were plated in 24‐well plates, cultured with indicated small molecules, and then collected and analyzed at designated time points. One‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test was used to calculate statistical significance between CHIR alone and CHIR plus rapamycin–treated cells at each time point (n=4; *P<0.05, **P<0.01). C, Analyzing the dynamic change of cell viability when initial seeding density is much lower. Single H9 cells (1.5×104/well) were plated in 24‐well plates, cultured with indicated small molecules, and then collected and analyzed at designated time points. One‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test was used to calculate statistical significance between CHIR alone and CHIR plus rapamycin–treated cells at each time point (n=4; **P<0.01; NS means no significant difference). D and E, Cell cycle and BrdU incorporation analysis of hESCs with different treatments at day 2 (n=4). F through H, The cell death level was analyzed by a different method. Analyzing the cell death levels of hESCs with corresponding treatment by measuring the extent of PARP cleavage (F), intracellular caspase 3/7 activity (n=5) (G), and annexin V/PI staining (n=6) (H) (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). I, Annexin V/PI staining and Western blot analysis of cell death of hESCs with z‐VAD addition (n=4; **P<0.01). J, Annexin V/PI staining analysis of the apoptotic level of hESCs with si‐mTOR or siTSC1/2 treatment at day 3 (n=5; **P<0.01). CHIR indicates CHIR99021; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; Rapa, rapamycin; si‐NC, negative control siRNA; z‐VAD, z‐Val‐Ala‐Asp (OMe)‐fluoromethylketone (z‐VAD‐FMK).
