Figure 3.
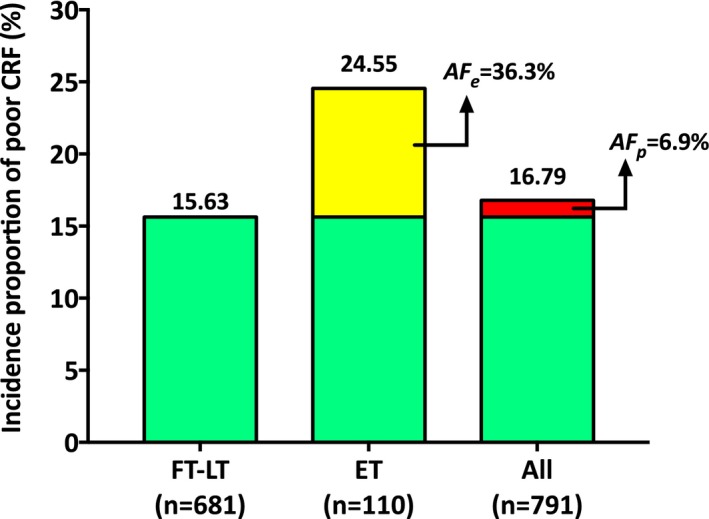
Incidence proportions of poor cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) through adolescence to young adulthood, among participants who were born full term (FT), late term (LT), or early term (ET) and in the whole study population (All). Yellow portion of the bar depicting the incidence proportion of poor CRF among the ET group illustrates the magnitude of the attributable fraction among the exposed: AF e=[(24.55−15.63)/24.55]×100=36.3%. Likewise, the red portion of the bar depicting the incidence proportion of poor CRF among all participants illustrates the magnitude of the population attributable fraction: AF p=[(16.79−15.63)/16.79]×100=6.9%. Incidence proportions were adjusted for sex, participants' age at the time of CRF, age×sex interaction terms, cohort, birth weight Z scores, socioeconomic status, delivery mode, breastfeeding, and maternal age, body mass index, and smoking. The AFs were estimated according to the method recommended by Greenland and Drescher49 (implemented in STATA with the command punaf) and could be also approximated by the following equations: AF e=(RR−1)/RR and AF p=[(RR−1)/RR]×Pe, commonly used in cohort studies, where RR is the multivariable adjusted risk ratio of poor CRF for ET vs FT−LT (ie, 1.57) and Pe is the proportion of individuals with poor CRF who were born ET (or case fraction).
