Figure 6.
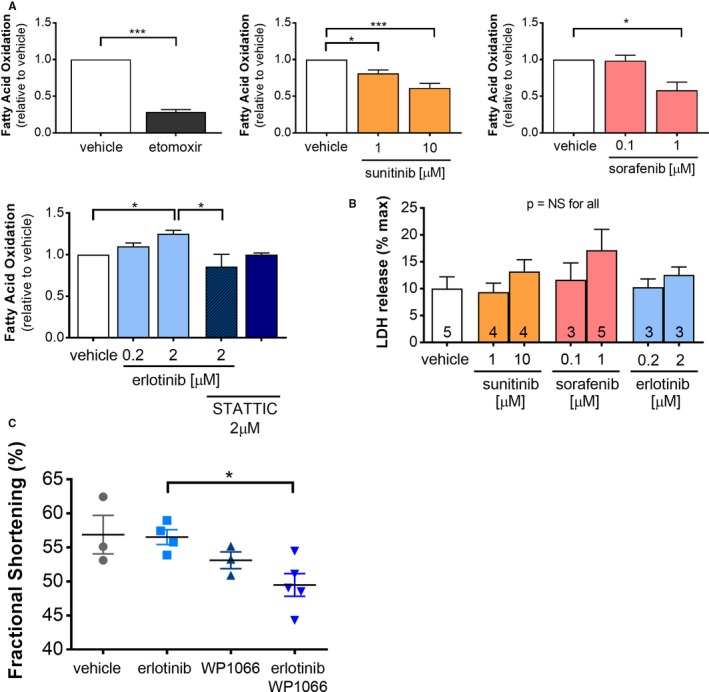
Co‐administration of a STAT inhibitor abrogates erlotinib‐induced increase in cardiomyocyte fatty acid oxidation in vitro and impairs contractile function in vivo. A, Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (n=4 independent experiments) were treated with vehicle, the carnitine phosphatoyl transferase inhibitor, etomoxir, or kinase inhibitors (including the STAT inhibitor, STATTIC) for 24 h, then fatty acid oxidation was assayed using 14C‐oleate. B, Cell death in NRVMs was assayed by LDH release (n=3–5 independent experiments, as indicated). C, Female FVB mice were treated with vehicle, erlotinib, and/or the STAT inhibitor WP1066 for 7 days and contractile function was assessed using conscious echocardiography. Groups for all experiments were compared using 1‐way ANOVA, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. LDH indicates lactate dehydrogenase; NRVMs, neonatal rat ventricular myocytes; NS, not significant; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
